QuantumScape is a U.S.–based advanced battery technology company focused on developing next-generation solid-state lithium-metal batteries intended primarily for electric vehicles (EVs). The company’s mission is to deliver higher energy density, faster charging, improved safety, and lower cost compared to conventional lithium-ion battery systems. While still pre-commercial, QuantumScape has forged partnerships with major automotive OEMs and battery materials firms, positioning itself as a potential enabler of the EV transition. The firm is headquartered in San Jose, California and trades on the New York Stock Exchange under ticker QS. Given its early stage and technology-risk profile, QuantumScape currently operates at a loss, as it transitions from R&D toward commercialization. Its strategic focus includes scaling manufacturing, reducing hardware cost, and monetizing via licensing or cell sales.

2. Most Recent Earnings (Q3 FY2025)
For the quarter ended September 30, 2025, QuantumScape reported a GAAP net loss of US$105.8 million (roughly –US$0.18 per share) compared with a loss of ~US$119.7 million in the same quarter the prior year. Its adjusted EBITDA loss was approximately US$61.4 million, in line with or slightly better than expectations. The company introduced a new metric, “customer billings,” totaling approximately US$12.8 million in Q3, reflecting invoices issued to partners though not recognised as revenue under U.S. GAAP. QuantumScape reiterated guidance for the full year of FY2025: adjusted EBITDA loss of roughly US$245-260 million, capital expenditures of ~US$30-40 million, and it expects its cash runway to extend into the end of the decade. Analysts had expected a loss of around –US$0.20 per share and the company slightly beat. While the financials remain loss-making, the improvement in loss magnitude, the launch of the billings metric, and the extended cash runway were viewed as positive signs of execution.
3. Origins, Founding, Funding, Products & Headquarters
QuantumScape was founded in 2010 by Jagdeep Singh, Tim Holme and Fritz Prinz at Stanford University. The founders combined expertise in computer science, mechanical/materials engineering and electro-chemistry. The company is headquartered in San Jose, California. Over the years, QuantumScape has raised large amounts of funding via venture capital, strategic investments (notably a significant investment from Volkswagen Group), and ultimately via a SPAC merger in 2020 that allowed its listing. Its product focus is on a solid-state lithium-metal battery cell technology: the cell uses a lithium-metal anode and a solid or ceramic separator (rather than the conventional liquid electrolyte structure), enabling high volumetric energy density, faster charge times and improved safety characteristics relative to current lithium-ion batteries. The firm is moving toward “QSE-5” cell versions and has announced sample shipments and collaboration programs with automotive partners. Key competitors include other advanced battery firms (see section below). The company’s strategy involves scalable manufacturing via its “Eagle Line” pilot line and a capital-light licensing model where it provides technology and manufacturing support to licensees or partners.
4. Market & Growth Outlook
QuantumScape operates in the broader battery technology market, and more specifically the niche of solid-state battery (SSB) technology for electrified vehicles and other energy storage applications. According to market research, the global solid-state battery market size was estimated at roughly US$1.18 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach about US$15.07 billion by 2030, implying a CAGR of approximately 56.6% between 2025-2030. Another source projects a CAGR of ~41–42% over the longer term (to 2032/2035). The electric vehicle battery market more broadly is far larger (hundreds of billions of dollars by 2030), and SSB is considered a potentially disruptive subset given its improved performance metrics. For QuantumScape, the opportunity lies in capturing a portion of that SSB market by licensing technology or selling cells to OEMs, thereby benefiting from the expected growth in EV penetration, the shift toward higher energy density and faster charging, and increased demand for safer, lighter systems.
5. Competitors
QuantumScape faces competition from both traditional lithium-ion battery developers/manufacturers and other firms focusing on next-generation solid-state technologies. Key competitors include:
- Solid Power, Inc., which is also developing solid-state batteries and has partnerships with automotive OEMs.
- Samsung SDI Co., Ltd. and other large battery makers (e.g., LG Energy Solution, CATL) that may bring advanced battery chemistries or solid-state variants to market.
- Smaller/alternative technology firms also attempting to commercialize solid-state/next-gen battery technology. In this competitive landscape, scale-up risk, manufacturing cost, yield, automotive qualification and licensing potential are all major hurdles.
6. Unique Differentiation
QuantumScape’s key differentiators relative to many competitors include:
- A single-digit (so far) sample cell shipping of its QSE-5 “B1” version using its proprietary “Cobra” ceramic separator process, which management claims enables much higher cell energy density and faster charging.
- A strategic partnership with Volkswagen/PowerCo/Audi/Ducati, using its cells in a high-visibility application (Ducati V21L motorcycle) to demonstrate real-world performance.
- The business model emphasis on a “capital‐light” licensing/roll-out strategy rather than building enormous vertically-integrated manufacturing alone; this means QuantumScape can potentially scale via partner network while limiting its fixed-capital burden.
- An extended cash runway: As of Q3 2025 the company stated it ended the quarter with ~US$1.0 billion liquidity and projects that this cash will last through the end of the decade (subject to execution). These differentiators provide the company with a solid technology-story and execution narrative, though commercialization remains a meaningful challenge.
7. Management Team (Max 3)
- Dr. Siva Sivaram, President & CEO. He joined QuantumScape in February 2024 and leads the company’s strategic direction, technological development and commercialization efforts.
- Kevin Hettrich, Chief Financial Officer. He is responsible for the company’s financial operations, reporting, investor relations, and managing the liquidity/cash-runway strategy.
- Jagdeep Singh, Executive Chairman (Founder). While no longer the day-to-day CEO, he founded the company and serves in a senior leadership capacity, guiding corporate governance and strategic partnerships.
8. Financial Performance Overview (Last 5 Years)
QuantumScape remains in a pre-commercial phase, which means its revenue is minimal or essentially nil under U.S. GAAP and losses are ongoing. Over the last five years, the company has invested heavily in research, development and pilot manufacturing infrastructure, with operating losses and negative earnings each year. For example, in Q3 2025 the net loss was US$105.8 million, improved from US$119.7 million in the same quarter of 2024. As a result, revenue growth cannot yet be meaningfully assessed (there is no significant product revenue yet). The lack of revenue means typical metrics like earnings growth or net income CAGR are not meaningful in the traditional sense; instead the story is one of narrowing losses, improving metrics (like billings) and extending the cash runway. On the balance sheet, as of September 30, 2025, QuantumScape reported approximately US$1.015 billion in current assets (including cash & marketable securities ~US$1.0 billion) and total assets of ~US$1.343 billion; total liabilities were ~US$127 million, giving stockholders’ equity of ~US$1.216 billion. The strong liquidity and modest liabilities demonstrate a relatively healthy financial base for a pre-commercial company, though until commercialisation begins the risk remains high. In summary, over the last 5 years QuantumScape has:
- Invested heavily and incurred persistent losses;
- Improved its cost profile and narrowed its loss trajectory in recent quarters;
- Built a solid cash/liquid securities base to support its roadmap;
- Yet not achieved meaningful product revenue or net income growth.
9. Bull Case
- QuantumScape’s solid-state battery technology could unlock dramatic improvements in EV range, charging speed and cost, providing a step-change advantage over incumbent lithium-ion batteries.
- If commercialised and scaled, QuantumScape’s licensing/partner-model could generate strong royalty or revenue streams with relatively low incremental capital investment, enabling high leverage once the model takes off.
- The extended cash runway and recent execution milestones (sample shipments, partner engagements, billings metric) give the company enough runway to de-risk key milestones and reach a commercialization inflection without immediate dilution.
10. Bear Case
- The technology and manufacturing risk remains substantial: scaling solid-state batteries to high yield, automotive grade reliability and cost competitiveness is unproven at scale; delays or performance shortfalls could derail the story.
- The market expectations are high, and much of the company’s valuation is premised on future commercialisation; any misstep in partner qualification, yield, cost per kWh or safety could lead to sharp multiple contraction.
- Given the company currently lacks meaningful product revenue, it remains dependent on raising capital or achieving partnerships/licensing deals; although the cash runway is extended, further dilution remains a potential risk if commercialization takes longer than expected.
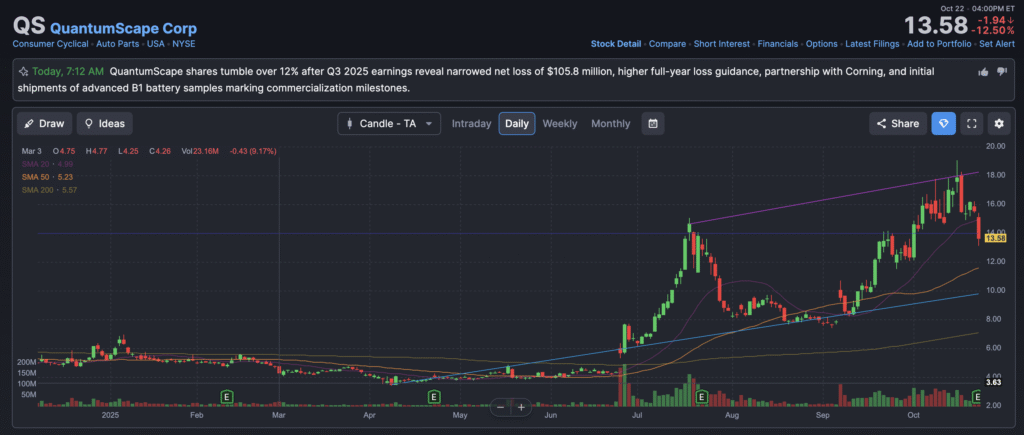
The stock is in a long term stage 1 consolidation zone (neutral) on the monthly and weekly charts. The daily chart is in stage 4 bearish markdown and has some support in the current $13 range, and should get to $15 zone thanks to lower losses in the short term. This is a very long term stock so I am not buying yet.