General Motors (NYSE: GM) – Driving the Future of Mobility
General Motors Company (GM) is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing vehicles under brands like Chevrolet, GMC, Cadillac, and Buick. Founded in 1908, GM is a legacy player transitioning aggressively into electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies. The company designs, manufactures, and sells vehicles, as well as automotive parts and software platforms, with a growing emphasis on electric and connected vehicles. With a strong global presence, GM continues to invest in innovation, AI, and supply chain modernization. Its strategic focus is aimed at becoming an all-electric automaker by 2035.
Most Recent Earnings – Q2 FY2025 (Reported July 23, 2025)
In its Q2 2025 earnings, GM reported adjusted EPS of $2.48, significantly exceeding analyst expectations of $1.88. Revenue came in at $47.7 billion, up 9% year-over-year, and above consensus estimates of $45.9 billion. The strong performance was driven by higher North American vehicle deliveries, improved margins in EVs, and cost efficiencies. GM also raised its full-year 2025 adjusted EPS guidance to a range of $9.00–$10.00 from $8.00–$9.00 and now expects EBIT-adjusted to be at the higher end of $12–$14 billion. For Q3 2025, GM forecasts revenue growth of 6–8% and expects further improvement in EV margins as battery costs decline.
Founding, Founders, Funding, Products, and Headquarters
GM was founded in 1908 in Flint, Michigan, by William C. Durant, a visionary businessman who consolidated several automobile companies. It quickly grew into a global behemoth by acquiring marquee brands and pioneering mass production methods alongside competitors like Ford. Headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, GM remains a symbol of American industrial strength.
The company has undergone multiple financial transformations over its history, including a high-profile bankruptcy and bailout during the 2008 financial crisis. GM returned to public markets in 2010 through a $20.1 billion IPO—the largest at the time. Today, GM’s capital allocation focuses on electrification, software, and autonomous technologies. It has invested over $35 billion in EV and AV development through 2025.
GM’s vehicle portfolio includes traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) models and newer electric models such as the Chevrolet Bolt EUV, Cadillac Lyriq, and GMC Hummer EV. Its software and connected services business—particularly the Ultifi platform—is emerging as a new growth lever. GM’s key competitors include Ford, Stellantis, Toyota, Tesla, and Hyundai.
The EV and Autonomous Vehicle Market
GM operates in a rapidly transforming global automotive market with strong tailwinds in electrification and autonomy. The global EV market was valued at ~$500 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach over $2.3 trillion by 2030, representing a CAGR of over 23%. Government mandates, emission regulations, and infrastructure investments are accelerating EV adoption across North America, Europe, and Asia.
In parallel, the autonomous vehicle (AV) market—where GM operates via its Cruise subsidiary—is projected to surpass $800 billion by 2030. However, this sector is maturing slower than expected due to regulatory hurdles and high R&D costs. GM remains committed to deploying AVs in ride-hailing and delivery services, especially in urban centers.
EV Competition and Market Pressures
GM faces intense competition from legacy automakers like Ford and Toyota, as well as disruptive EV-native players like Tesla, Rivian, and BYD. Tesla still dominates the U.S. EV market with roughly 50% share, but GM is closing the gap through Ultium battery partnerships, vertical integration, and an expanding EV lineup. International competition from Chinese EV brands like Nio and XPeng also poses challenges to GM’s global expansion plans.
GM’s Strategic Differentiation
What sets GM apart is its vertically integrated Ultium battery platform, scalable across SUVs, pickups, and sedans, giving it flexibility and cost advantages. GM’s software-defined vehicle strategy, led by its Ultifi operating system, aims to turn cars into monetizable software platforms. Additionally, its investment in Cruise for AV development provides a potential leapfrog advantage if commercial autonomy scales in the late 2020s.
Key Executives and Leadership Team
Mary Barra, GM’s CEO since 2014, is the first female CEO of a major global automaker. She has championed the company’s pivot toward electrification and autonomous driving. Under her leadership, GM has aggressively exited unprofitable markets and restructured operations for agility. Paul Jacobson, CFO since 2020 and formerly at Delta Air Lines, has played a critical role in tightening cost controls and maintaining a strong balance sheet. Doug Parks, EVP of Global Product Development, leads EV innovation and battery technology, playing a central role in Ultium platform execution.
Financial Performance (Last 5 Years)
Over the past five years, GM has demonstrated solid financial performance despite macroeconomic headwinds, COVID disruptions, and supply chain shocks. Revenues grew from $122 billion in 2020 to $174 billion in 2024, a CAGR of ~9%. Earnings per share rose steadily, supported by cost discipline, high-margin SUV and truck sales, and early EV momentum.
Adjusted EBIT grew from $8.3 billion in 2020 to $13.4 billion in 2024. Net income followed suit, reaching $11.5 billion in 2024. GM’s balance sheet remains healthy, with ~$30 billion in cash and a net debt-to-EBITDA ratio under 1.2x. Capex remains elevated as GM invests ~$10 billion annually into EV plants, battery development, and autonomous initiatives.
Bull Case for GM Stock
- Strong EV momentum and scalable Ultium platform will drive market share gains and higher margins.
- Software and services revenue via Ultifi could become a high-margin recurring income stream by 2027+.
- Cruise could unlock significant value if autonomous commercialization accelerates in urban markets.
Bear Case for GM Stock
- Execution risk in transitioning from ICE to EV—delays or cost overruns could hurt margins and credibility.
- EV pricing pressure from Tesla, BYD, and Chinese OEMs could squeeze profits in GM’s core growth segments.
- Cruise AV unit remains unprofitable and faces regulatory, technical, and public trust challenges.
Analyst Reactions to Q2 2025 Earnings
Following Q2 earnings, analysts at Morgan Stanley raised their price target on GM to $55 from $48, citing margin improvements in EVs. Goldman Sachs maintained a “Buy” rating and increased their FY25 EPS estimate by 12%. Conversely, UBS maintained a “Neutral” rating, noting concerns about Cruise’s burn rate and potential write-down risks. Overall, sentiment remains bullish on GM’s transition strategy, though execution risk is priced in.
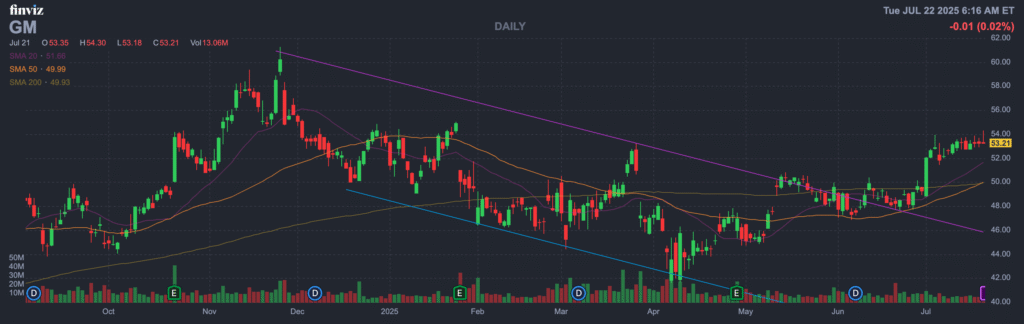
The stock is in a stage 1 consolidation on the monthly and on the daily chart is in a stage 2 markup (Bullish). The daily chart is bullish as well, but post earnings price action will determine the price momentum to $55. There is a lot of resistance at that level, which might mean a move lower again after that.