Executive Summary:
Ford Motor Company is a prominent American multinational automaker headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan. It is renowned for pioneering mass production techniques, notably the moving assembly line, which revolutionized the automotive industry. Ford markets vehicles under the Ford brand and luxury vehicles under the Lincoln brand and has a global presence with manufacturing and sales operations worldwide. The company is actively transitioning toward electric vehicles and innovative technologies while continuing to produce its iconic models.

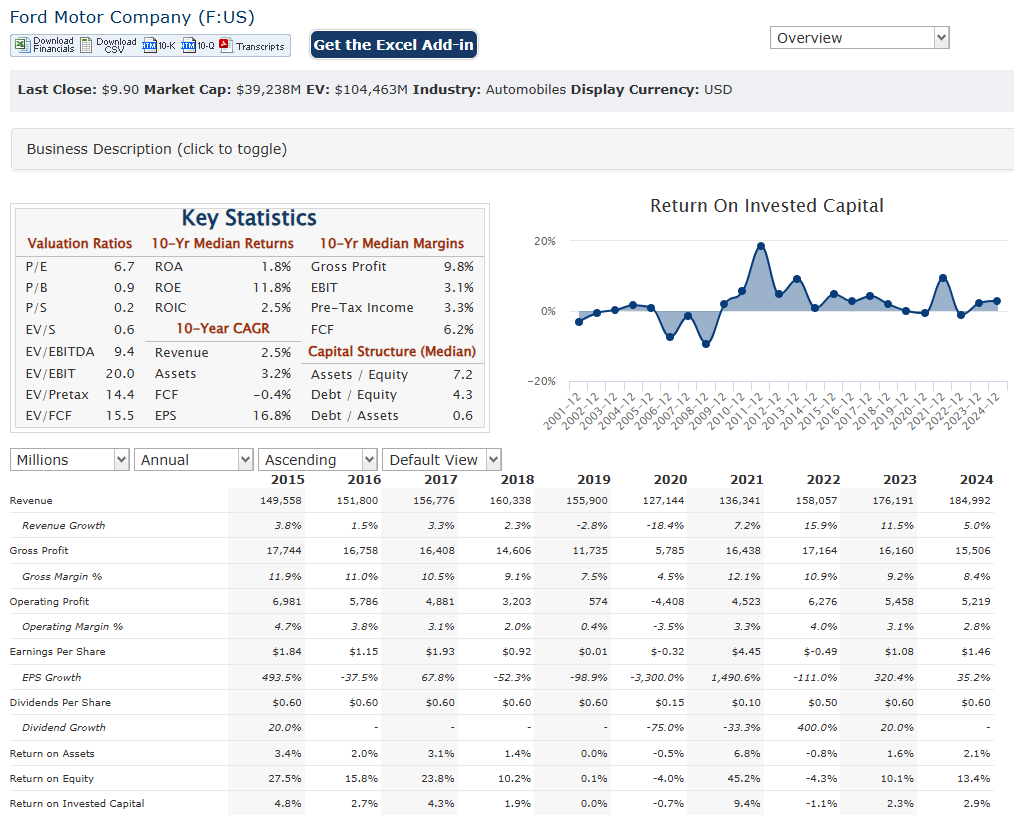
Ford Motor Company reported a revenue of $48.2 billion, demonstrating a 5% year-over-year increase. The adjusted EPS was $0.39. For the full year 2024, Ford’s revenue reached $185 billion. An adjusted EBIT expectation of $7.0 billion to $8.5 billion.
Stock Overview:
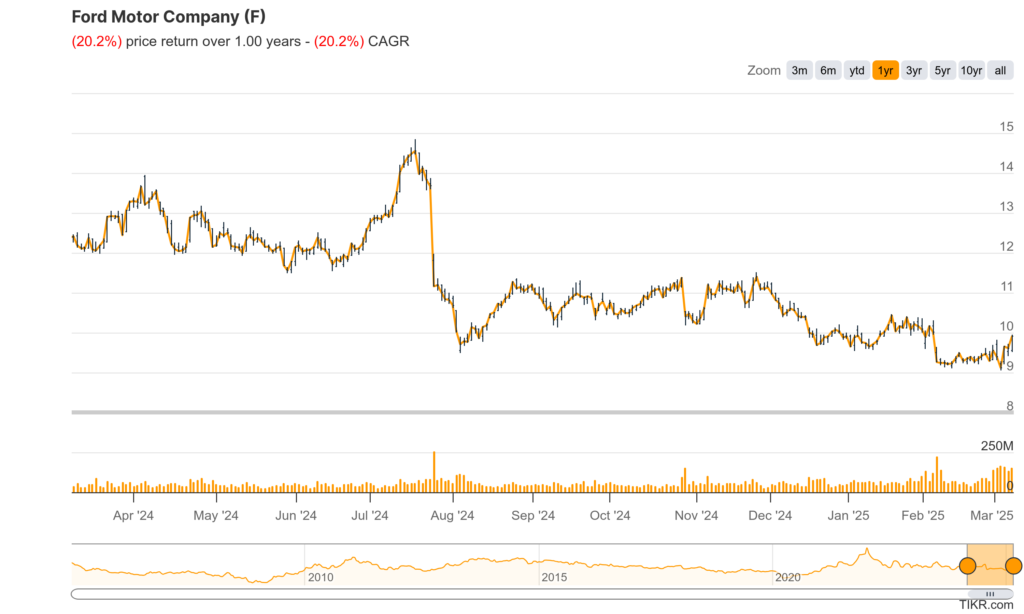
| Ticker | $F | Price | $9.90 | Market Cap | $39.24B |
| 52 Week High | $14.85 | 52 Week Low | $9.06 | Shares outstanding | 3.89B |
Company background:
Ford Motor Company, a cornerstone of the American automotive industry, was founded by Henry Ford in Detroit, Michigan, and incorporated on June 16, 1903. Henry Ford’s vision, coupled with the financial backing of early investors like Alexander Y. Malcomson, was crucial to the company’s inception. The early funding allowed Ford to pursue his innovative ideas, most notably the development of the moving assembly line, which revolutionized mass production.

Ford’s product line is diverse, encompassing a wide range of vehicles. The company produces popular models like the F-150 truck, the Mustang, and various SUVs. Ford markets luxury vehicles under the Lincoln brand. Ford has intensified its focus on electric vehicles, with models like the Mustang Mach-E and the F-150 Lightning demonstrating its commitment to the future of automotive technology.
Ford operates in a highly competitive market, facing challenges from both traditional automakers and emerging electric vehicle manufacturers.
- General Motors (GM)
- Toyota
- Volkswagen Group
- Stellantis
- Tesla
- Hyundai Motor Group
These companies vie for market share in various segments, from traditional gasoline-powered vehicles to the rapidly expanding electric vehicle market. Ford’s headquarters are located in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit, which has long been the heart of the American automotive industry.
Recent Earnings:
Ford reported a revenue of $48.2 billion, representing a 5% year-over-year increase. The full-year 2024 revenue reached $185 billion, also demonstrating a 5% growth compared to the previous year.
The adjusted Earnings Per Share (EPS) for the fourth quarter was $0.39. It is also important to note that GAAP net income was $1.8 billion, or $0.45 per share.
Ford Blue (traditional combustion engine vehicles), Ford Model e (electric vehicles), and Ford Pro (commercial vehicles and services). Ford Pro demonstrated strong performance, with EBIT margins and increased revenue. Ford Model e is still in a heavy investment phase, showing large losses, as the company invests in future EV products. Ford’s adjusted EBIT expectation of $7.0 billion to $8.5 billion, and adjusted free cash flow of $3.5 billion to $4.5 billion. This provides insights into the company’s projected financial performance and strategic direction. Ford is also focusing heavily on improving quality and cutting costs.
The Market, Industry, and Competitors:
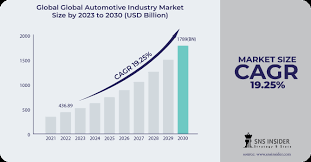
Ford Motor Company operates within the global automotive market, a vast and dynamic sector undergoing a significant transformation. This market encompasses the production, distribution, and sale of passenger cars, trucks, SUVs, and commercial vehicles. It’s characterized by intense competition, evolving consumer preferences, and increasing regulatory pressures related to emissions and sustainability. The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies is reshaping the industry, requiring established automakers like Ford to adapt and innovate rapidly. Additionally, factors such as global economic conditions, raw material prices, and supply chain disruptions significantly impact the market’s performance.
The automotive market is expected to experience substantial growth, driven primarily by the increasing adoption of EVs and the expansion of mobility services. Projections indicate a significant rise in EV sales, with some estimates suggesting they could account for a substantial portion of new vehicle sales by 2030. The market is also witnessing the emergence of new players, particularly in the EV space, intensifying competition. For Ford, this means continued investment in its Ford Model e division, developing advanced battery technologies, and expanding its EV production capacity. The CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) for the EV segment is projected to be very high, estimates vary depending on the source, but many project a CAGR of over 20% through 2030.
Unique differentiation:
Ford Motor Company operates in a highly competitive global automotive market, facing established rivals and emerging challengers. Traditional competitors like General Motors (GM) and Stellantis remain significant players, offering a wide range of vehicles across various segments. GM, in particular, is a direct competitor in the North American market, with similar product lines and a shared history. Toyota, another major competitor, excels in reliability and fuel efficiency, posing a strong challenge in the global market, especially in hybrid and fuel-efficient vehicles. Volkswagen Group, a global automotive powerhouse, competes across numerous segments and regions, with a diverse portfolio of brands. These established automakers are all heavily investing in electric vehicle technology, directly challenging Ford’s Model e division.
The competitive landscape is also being reshaped by the rise of electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers. Tesla, a pioneer in the EV space, has disrupted the market with its innovative technology, software integration, and direct-to-consumer sales model. Tesla’s focus on high-performance EVs and its advanced battery technology present a formidable challenge to Ford’s EV ambitions. Emerging EV companies like Rivian and Lucid Motors are also vying for market share, albeit in niche segments. Furthermore, Hyundai and Kia have made significant strides in the EV market, providing strong competition with vehicles that are often seen as high value. These competitors are forcing Ford to accelerate its EV development, enhance its software capabilities, and adapt its manufacturing processes to remain competitive in the rapidly evolving automotive landscape.

“Built Ford Tough” Brand and F-Series Dominance: Ford has cultivated a powerful brand image, particularly with its “Built Ford Tough” slogan, which resonates strongly with truck and SUV buyers. The F-Series trucks have consistently been best-sellers, demonstrating Ford’s strength in this highly profitable segment. This strong brand recognition and customer loyalty in the truck market is a very strong differentiator.
Ford Pro and Commercial Solutions: Ford’s focus on commercial vehicles and services through Ford Pro is a key differentiator. This segment provides comprehensive solutions for commercial customers, including electric vehicles, software, and services, which sets Ford apart from many competitors. This focus on commercial customers, and providing a total package of services, is a strong differentiating factor.
Management & Employees:
James D. Farley, Jr.: As President and Chief Executive Officer, Farley is driving Ford’s strategic direction, with a strong emphasis on electric vehicles and digital innovation. He is a key figure in Ford’s efforts to compete in the rapidly evolving automotive landscape.
William Clay Ford, Jr.: Serving as Executive Chair, William Clay Ford, Jr. plays a vital role in the company’s long-term vision and maintains the Ford family’s involvement in the business.
Kumar Galhotra: Serving as Chief Operating Officer, Galhotra is responsible for the companies daily operations.
Ford’s management team reflects a blend of experienced automotive professionals and leaders with expertise in technology and digital transformation. The company is focused on strengthening its position in the electric vehicle market, while also maintaining its core business of traditional vehicles.
Financials:
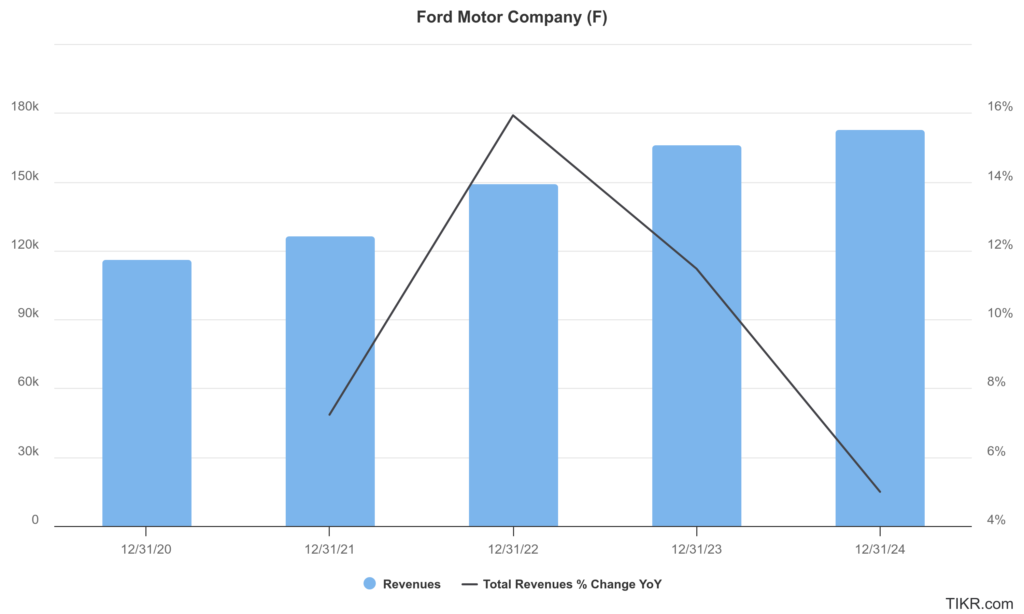
Ford Motor Company reported revenue increased by 11% to $176 billion compared to the previous year. Ford reported a net income of $4.3 billion, marking an improvement over previous years. However, the company faced challenges, such as a non-cash accounting loss in the fourth quarter of 2023, which impacted its quarterly net income. The adjusted EBIT for 2023 was $10.4 billion, which was essentially flat compared to the previous year.
The company has been focusing on transforming its operations to adapt to the evolving automotive landscape, particularly with its Ford+ plan aimed at electric and connected vehicles. This strategic shift is crucial for maintaining financial health and competitiveness in the long term.
Ford’s performance has been mixed due to the variability in net income over the years. The company’s revenue CAGR indicates a positive trend, especially with recent growth rates. Ford’s financial performance is influenced by factors such as market conditions, technological shifts, and operational efficiencies. Ford’s ability to adapt and innovate will be key to sustaining growth and improving financial metrics.
Technical Analysis:
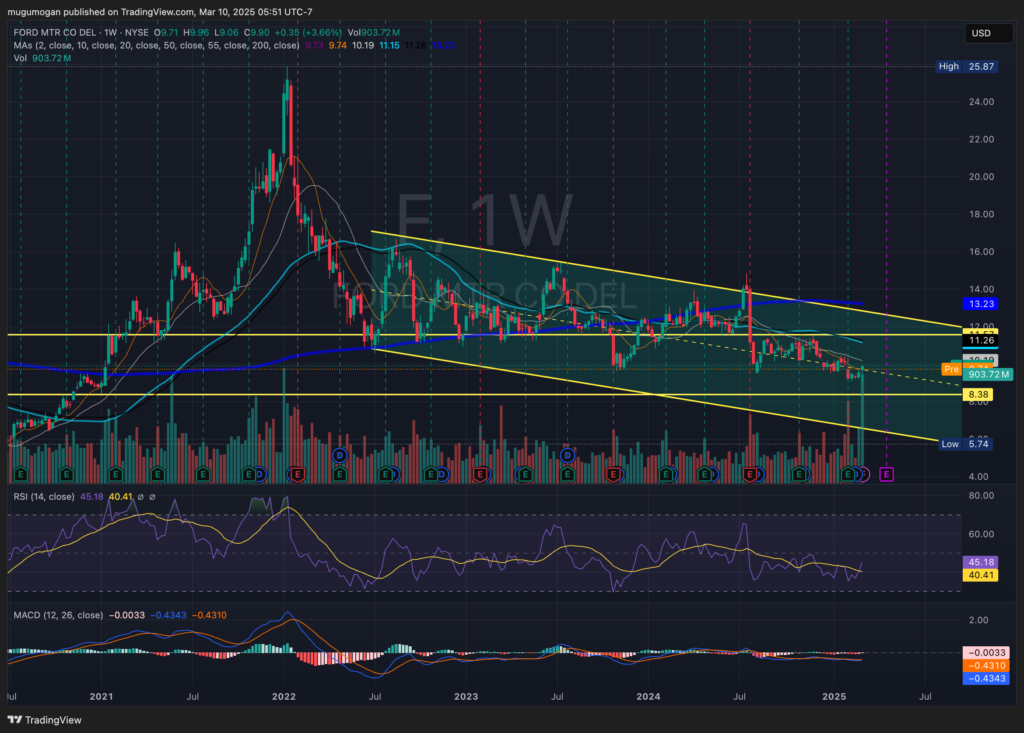
The stock is in a stage 4 decline on the monthly and weekly charts. The daily chart shows some support at the $8.38 range, where it could reverse, but this is not a stock for the short term.
Bull Case:
Successful EV Transition: A major component of the bull case hinges on Ford’s ability to effectively execute its electric vehicle strategy. If Ford can successfully scale its EV production, deliver compelling EV models, and gain market share in the rapidly growing EV sector, it could drive substantial revenue growth. Specifically, if Ford can improve the profitability of its Ford Model e division, that would be a very large positive.
Valuation and Dividend: Ford’s stock often trades at a relatively low valuation compared to the broader market. This could present an opportunity for investors seeking value. Ford also provides a dividend, which can be attractive to income-focused investors.
Strategic Adaptability: Ford’s management has demonstrated a willingness to adapt to changing market conditions. This includes adjusting EV production plans in response to shifting consumer demand and focusing on profitable segments like hybrids. The ability to navigate a changing market is very important for an automotive company.
Bear Case:
Intense Competition and Pricing Pressures: The automotive industry is highly competitive, and increasing competition in the EV space could lead to pricing pressures and reduced profit margins. If Ford is unable to maintain its market share or compete effectively on price, its profitability could suffer.
High Debt and Investment Costs: Ford carries a substantial amount of debt, and the significant investments required for its EV transition could strain its financial resources. If the company is unable to generate sufficient cash flow to manage its debt and fund its investments, it could face financial difficulties.
Quality and Warranty Issues: Any major quality or warranty issues with new EV models, or existing ICE models, could damage Ford’s reputation and lead to increased costs.