Executive Summary:
Maplebear Inc is the company behind the popular grocery delivery service Instacart. Instacart allows customers to order groceries from partnering retailers through their app and website. With a network of personal shoppers, Instacart delivers fresh produce and other household items to customers across the United States and Canada.

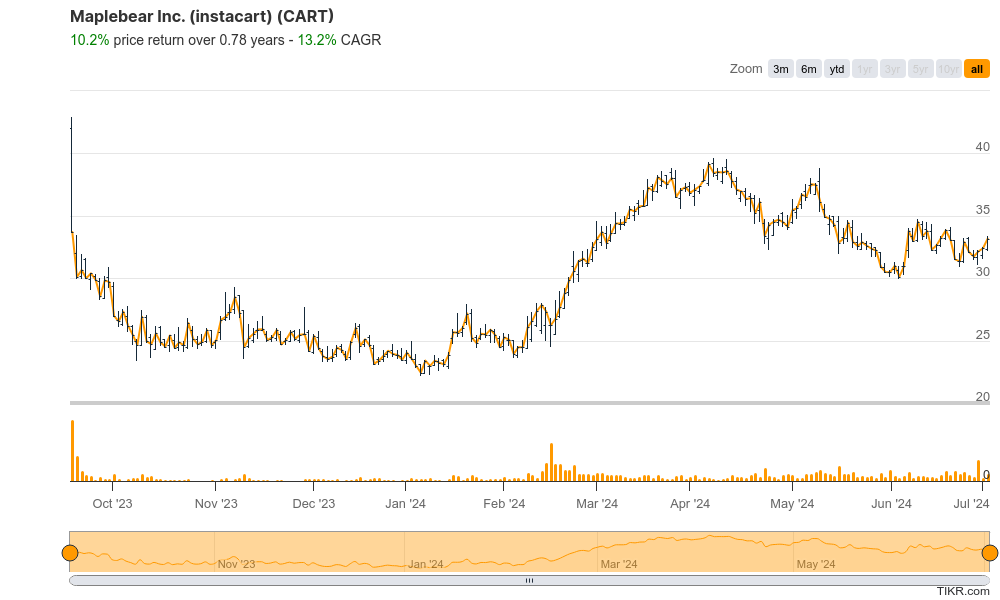
Maplebear reported earnings per share (EPS) of $0.43. Revenue for the trailing twelve months (TTM) sits at $3.1 billion.
Stock Overview:
| Ticker | $CART | Price | $34.13 | Market Cap | $9.03B |
| 52 Week High | $42.95 | 52 Week Low | $22.13 | Shares outstanding | 264.69M |
Company background:
Maplebear Inc., the company behind the well-known grocery delivery service Instacart, was founded in 2012 by tech veterans. Headquartered in San Francisco, California, the company has grown into a leader in the online grocery delivery market. Instacart utilizes personal shoppers to fulfill orders, ensuring fresh produce and other household items reach customers’ doorsteps across North America. Beyond customer-facing grocery delivery, Maplebear also offers software-as-a-service (SaaS) solutions to their retail partners, streamlining their online grocery operations.

Maplebear faces competition from several players in the online grocery delivery space. Major rivals include established retailers like Amazon Fresh and Walmart+ Grocery, as well as fellow delivery-focused companies like DoorDash and Uber Eats that have expanded into grocery delivery.
Recent Earnings:
Maplebear Inc revenue for the trailing twelve months (TTM) reached $3.1 billion, reflecting an 8% year-over-year increase. The company reported earnings per share (EPS) of $0.43. Aanalyst expectations of just $0.04, demonstrating a beat of $0.39 per share. The positive EPS for the quarter, the TTM EPS sits at -$5.36.
Forecasts predict EPS to reach $1.02 by the end of 2024, indicating continued improvement towards profitability.
The Market, Industry, and Competitors:
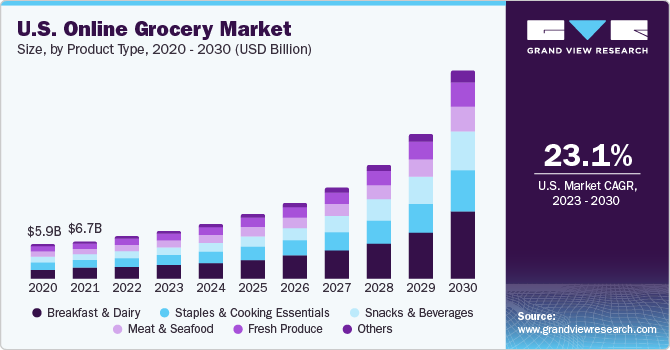
Maplebear Inc., through its Instacart platform, operates in the booming online grocery delivery market. They services are like lifestyles, increasing smartphone penetration, and growing consumer comfort with online shopping. Analysts project the global online grocery market to reach a staggering $1.4 trillion by 2030, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of around 14% over the next six years.
Time-pressed consumers are increasingly turning to online grocery delivery for convenience, while the expansion of delivery services to smaller towns and rural areas is opening up a wider customer base. The growing adoption of omnichannel retail strategies, where online and offline shopping experiences are integrated, is further propelling online grocery sales.
Unique differentiation:
Established Retailers: Retail giants like Amazon Fresh and Walmart+ Grocery leverage their existing infrastructure and vast customer base to offer competitive delivery services. These companies can often offer lower prices and faster delivery times due to their extensive fulfillment networks.
Delivery-Focused Companies: Companies like DoorDash and Uber Eats, initially known for restaurant delivery, have expanded into the grocery space. Their existing delivery infrastructure and large pool of drivers allow them to compete effectively, particularly in densely populated areas.
Regional Players: Several regional grocery chains and local delivery startups also compete for market share. These players often cater to specific demographics or offer specialized services, making them attractive options for certain customer segments.

Focus on Grocery-Specific Shopping Experience: Unlike DoorDash and Uber Eats that adapted their existing platforms for groceries, Instacart built its platform specifically for grocery shopping. This focus allows for a more tailored user experience, potentially including features like advanced product filtering, detailed product information, and integration with loyalty programs of partnered retailers.
Network of Trained Personal Shoppers: Instacart utilizes a network of trained personal shoppers who handpick groceries. This focus on quality control and attention to detail can differentiate them from competitors who might rely on gig workers with less training in selecting fresh produce or handling delicate items.
Management & Employees:
CEO and Chair: The current CEO and Chair of Maplebear Inc. is Fidji Simo.
Financials:
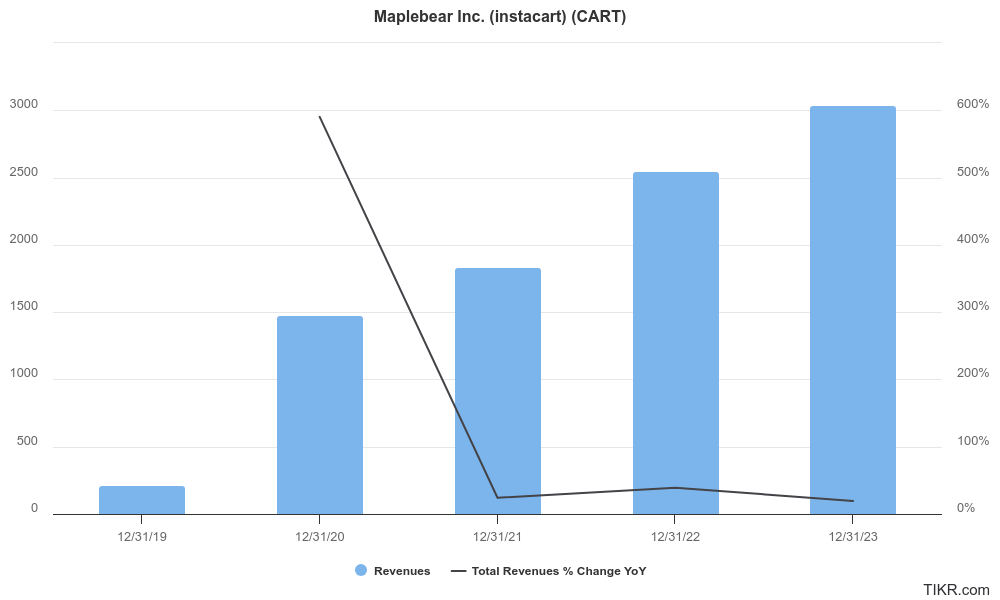
Maplebear Inc revenue has grown steadily, reflecting the increasing popularity of online grocery delivery. Year-over-year growth has averaged around 10.6%, indicating a healthy market with significant room for expansion. This translates to a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 14%.
Earnings per share (EPS) have shown negative growth over the past five years, with the average annual decline reaching an estimated 43.4%.
Maplebear likely carries a significant amount of debt to finance its operations and expansion. This is a common strategy for high-growth startups, but it will be crucial for Maplebear to demonstrate.

Technical Analysis:
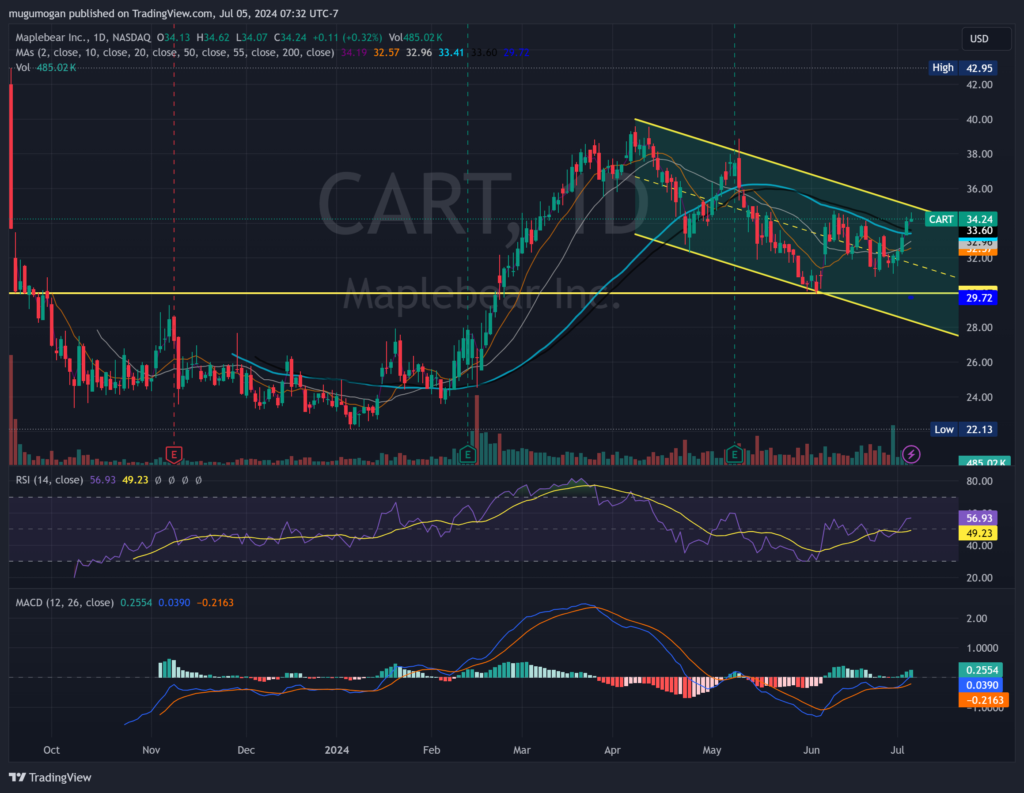
On the monthly chart, the stock has started to reverse after a long stage 4 markdown and is now in a stage 2 mark up and reversal. While still too early to tell on the weekly chart, the stage 2 markup is more clear on the daily chart with support at $29 and resistance in the $36 – $38 zone. We would enter the stock for a long term 2-3 year hold in the $30 – $35 levels
Bull Case:
Strong Brand & User Experience: Instacart boasts strong brand recognition and a user-friendly platform. Features like advanced product filtering and integration with loyalty programs can enhance the customer experience compared to competitors.
Focus on Quality: Instacart’s network of trained personal shoppers offers a potential advantage in terms of quality control and careful selection of fresh groceries.
Extensive Partnerships: Deep partnerships with a vast network of retailers allow Instacart to offer a wider product selection and potentially negotiate better pricing for customers.
Bear Case:
Operational Challenges: Managing a large network of personal shoppers and ensuring efficient delivery logistics can be complex and expensive.
Reliance on Retailers: Instacart relies heavily on partnerships with retailers. If these partnerships become strained or if retailers develop their own strong delivery platforms, it could negatively impact Instacart’s business model.
Consumer Sensitivity to Price: Grocery shopping is a cost-conscious activity. If competitors offer lower prices or faster delivery times, customers might be swayed away from Instacart.










