Executive Summary:
Coursera Inc. is a major online learning platform founded in 2012 by Stanford professors with the goal of providing accessible education worldwide. They collaborate with universities and other organizations to offer a wide range of courses, certificates, and even degrees. Coursera works in various fields including technology, business, and data science, and boasts over 142 million registered users. The company became a public benefit corporation and a B Corp in 2021.

Revenue hit $168.9 million, exceeding analyst expectations and reflecting a 19% increase year-over-year. Earnings per share (EPS) were positive at $0.06, marking a significant 250% jump compared to the same period last year. This suggests Coursera is narrowing its losses.
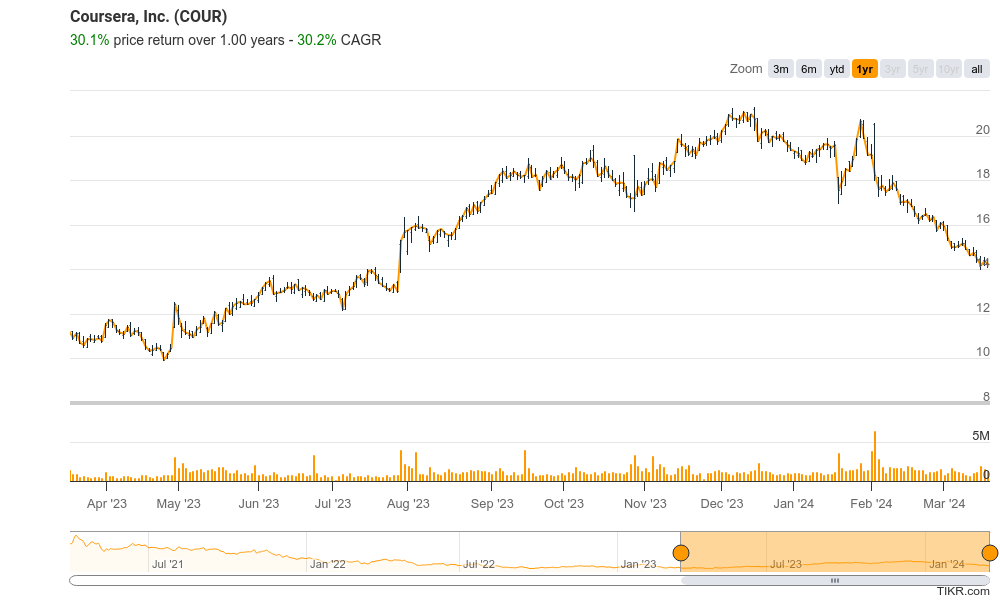
Stock Overview:
| Ticker | $COUR | Price | $14.22 | Market Cap | $2.23B |
| 52 Week High | $21.26 | 52 Week Low | $9.91 | Shares outstanding | 156.94M |
Company background:
Coursera Inc. was founded by Stanford computer science professors Daphne Koller and Andrew Ng. Their mission is to democratize education by providing universal access to high-quality learning experiences. Coursera initially secured funding from venture capitalists and corporations. This allowed them to expand their course offerings and collaborate with universities and other institutions to offer a wide range of educational content.

They offer learners various options, from individual courses and specializations to professional certificates and even full degrees. their commitment to social good and balancing profit-making with positive societal impact.
The company faces competition from several key players in the online learning arena, including Udemy, edX, Skillshare, and FutureLearn. Each platform offers a unique blend of courses, features, and target audiences. Coursera’s headquarters are located in Mountain View, California, placing them in the heart of the tech hub Silicon Valley.
The Market, Industry, and Competitors:
Coursera Inc thrives in the booming online learning market, fueled by the ever-increasing demand for upskilling, reskilling, and flexible learning avenues. This market caters to individuals seeking to stay competitive in the job market or pursue personal development goals. Coursera facilitates this by providing a platform for universities and other institutions to offer massive open online courses (MOOCs), specialization programs, certificates, and even full degrees.
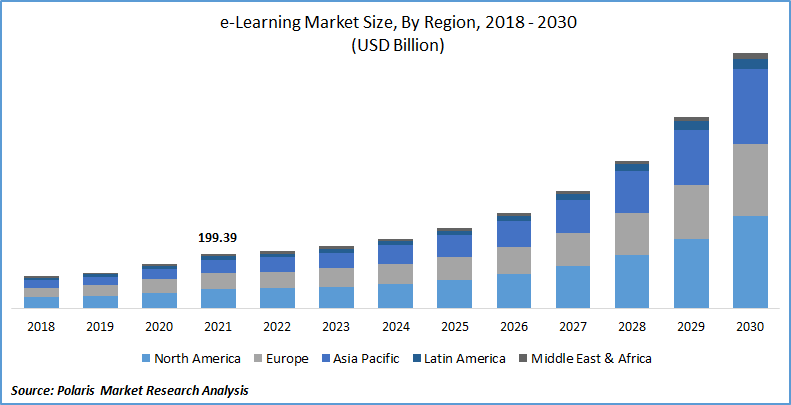
The online learning market is projected to experience tremendous growth, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) estimated to be around 11.6% between 2023 and 2030. This significant growth indicates a rising global demand for online education, creating a favorable environment for Coursera’s expansion in the coming years. As a major player in this space, Coursera is well-positioned to benefit from this rising tide in the online education sector.
Unique differentiation:
Coursera navigates a dynamic landscape populated by several well-established online learning platforms.
- Udemy: A titan in the online learning sphere, Udemy boasts a vast course library encompassing a wide range of professional development and creative skill-focused topics. They often cater to a more individual-instructor model.
- edX: Primarily known for its MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) offered in collaboration with prestigious universities and institutions like MIT and Harvard. edX leans towards a more academic course structure.
- FutureLearn: A prominent player in the European market, FutureLearn is known for its focus on UK universities and courses, making it a strong competitor for learners seeking European-accredited qualifications.

Coursera holds several potential differentiators compared to its online learning competitors:
- Strong University Partnerships: Coursera boasts collaborations with a vast network of prestigious universities and institutions like Stanford, Yale, and IBM. This allows them to offer learners access to high-quality, accredited courses and credentials directly from renowned educators.
- Degree Programs: Unlike some competitors focused on individual courses or certificates, Coursera has ventured into offering full online degrees in collaboration with universities. This caters to learners seeking a more comprehensive educational experience.
- Specialization Tracks: Coursera’s specialization tracks offer learners a curated sequence of courses designed to build specific skills in a particular area. This structured approach provides a more in-depth learning experience compared to isolated courses offered by some competitors.
- Focus on Employability: Many of Coursera’s courses and specializations are designed with a career-focused lens, aiming to equip learners with the skills needed for in-demand jobs. This focus on employability can be a significant advantage for learners seeking to advance their careers.
- B Corp Status: As a public benefit corporation (B Corp), Coursera signifies a commitment to balancing social good with financial goals. This focus on social impact might resonate with learners who want to support a company with a broader mission.
Management & Employees:
- Jeff Maggioncalda (President, Chief Executive Officer, and Director): Maggioncalda leads Coursera’s overall strategy and growth. He previously served as the founding CEO of Financial Engines Inc., bringing expertise in financial services and leadership.
- Shravan Goli (Chief Operating Officer): Goli oversees Coursera’s day-to-day operations, ensuring smooth execution across the company. He possesses experience in leading technology companies like DHI Group Inc.
Financials:
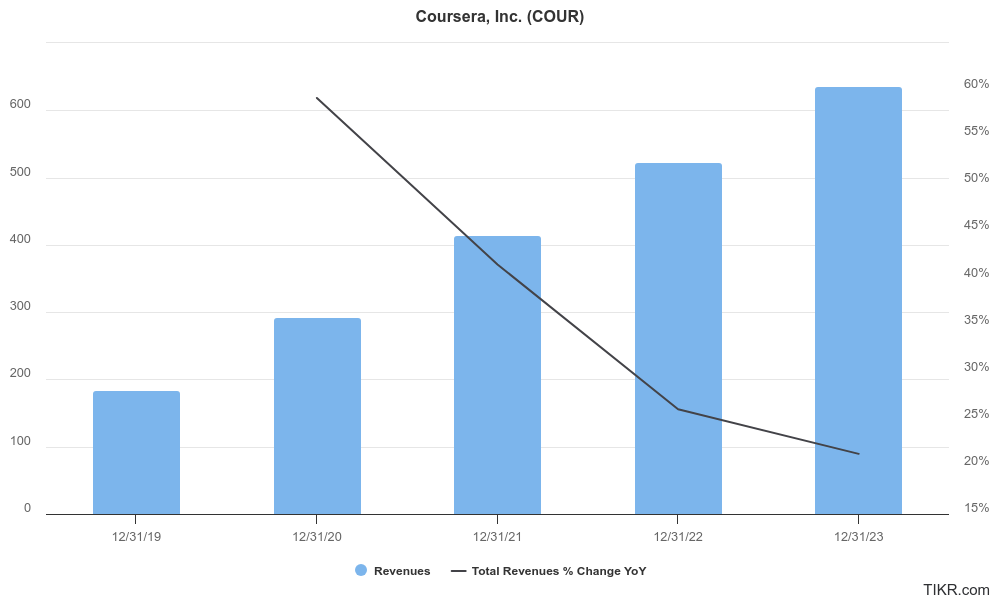
Coursera has experienced significant growth in revenue, solidifying its position in the online learning market. Revenue has consistently climbed year-over-year, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) estimated to be well above industry averages.
Coursera is still a relatively young company and has yet to achieve consistent profitability. While revenue has grown steadily, the company remains focused on user acquisition and market expansion. This has resulted in net losses in previous years. However, recent earnings reports indicate progress towards profitability, with a narrowing gap between revenue and expenses. The company is showing positive growth in Earnings Per Share (EPS), suggesting they are on the right track for future profitability.
Coursera’s balance sheet likely reflects a focus on growth. The company has likely invested heavily in technology infrastructure, content acquisition, and marketing initiatives to fuel user base expansion. This might translate to significant intangible assets and potentially higher debt levels.

Technical Analysis:
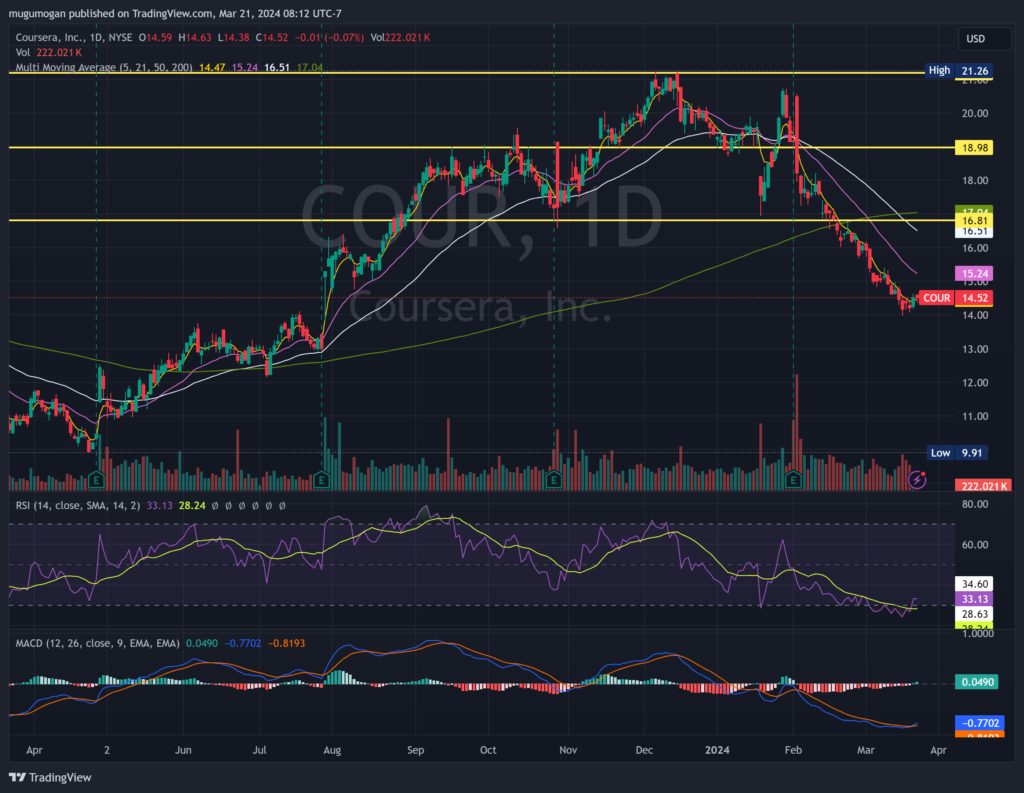
On the monthly chart, the stock is back in a stage 4 decline after a strong base. While the bounce is too early to call on the daily chart at $14.02, the stock has been testing that level multiple times. Until we get confirmation that the stock will cross the $15.23 levels, we will likely only take a small position to trade, not buy for the long term.
Bull Case:
- Soaring Demand for Online Learning: The online learning market is experiencing explosive growth fueled by the need for upskilling, reskilling, and flexible education options. This trend is expected to continue for the foreseeable future, creating a massive opportunity for Coursera.
- Progress Towards Profitability: Recent earnings reports show positive signs, with Coursera narrowing its losses and achieving EPS growth. This suggests the company is on the path to profitability in the near future, which can be attractive to investors seeking long-term value.
- Potential for Disruption: The online learning landscape is constantly evolving. Coursera’s ability to innovate and adapt with new technologies and learner preferences could position them as a disruptor in the education sector.
Bear Case:
- High Customer Acquisition Costs: Attracting new learners can be expensive, especially as competitors vie for attention. Coursera may need to invest heavily in marketing and promotions, impacting profitability in the short term.
- Content Quality Concerns: Relying on partnerships for content creation can lead to inconsistency. Maintaining high-quality course offerings across a broad range of subjects is crucial, and any lapses could lead to learner dissatisfaction and churn.
- Uncertain Long-Term Growth: While the online learning market is promising, its long-term growth trajectory is uncertain. If the demand for online education plateaus or new technologies emerge, Coursera’s business model could be challenged.
- Regulation and Accreditation: The online learning market is a relatively new frontier, and regulations and accreditation standards are still evolving. Changes in these areas could pose challenges for Coursera, especially regarding the recognition of online degrees.
- The challenge from AI – as ChatGPT and other AI tools get used more for customized learning, the need for Coursera reduces.
