Company Overview
Dell Technologies Inc. is one of the world’s largest technology companies, offering a broad range of products and services including personal computers, servers, storage, networking, cloud solutions, and IT consulting. Founded in 1984 by Michael Dell, the company has grown into a global leader in both consumer and enterprise IT markets. Dell operates through multiple segments including Infrastructure Solutions Group (ISG), Client Solutions Group (CSG), and VMware (until its spinoff in 2021). Its products serve corporations, governments, educational institutions, and consumers worldwide. Dell is headquartered in Round Rock, Texas, and employs more than 120,000 people globally.

Most Recent Earnings
On August 29, 2025, Dell reported earnings for Q2 FY2026. The company posted EPS of $2.09, above analysts’ expectations of $1.75, and revenue of $23.2 billion, compared to estimates of $22.6 billion. Revenue grew 7% year-over-year, driven by strength in AI-optimized servers and enterprise infrastructure demand, although client PC sales remained stable with limited growth. Gross margins expanded slightly due to higher-margin enterprise sales. For Q3 FY2026, Dell guided revenue in the range of $23.5–24.5 billion and EPS between $2.00–$2.20, while maintaining full-year revenue growth guidance of mid-to-high single digits.
Founding and Growth Journey
Dell was founded in 1984 by Michael Dell, who began building custom PCs from his dorm room at the University of Texas at Austin. Initially called PC’s Limited, the company grew rapidly with its direct-to-consumer sales model, bypassing retailers and selling directly to customers. By 1988, Dell went public, raising $30 million. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, Dell became one of the top PC manufacturers in the world, known for its efficient supply chain and low-cost production.
Over the years, Dell expanded beyond PCs into enterprise infrastructure. In 2016, it completed one of the largest tech mergers ever by acquiring EMC Corporation for $67 billion, creating Dell Technologies. This acquisition brought enterprise storage giant EMC, virtualization leader VMware, and cybersecurity firm RSA under Dell’s umbrella.

Products, Funding, and Competitors
Dell’s product portfolio spans laptops, desktops, workstations, servers, storage solutions, networking hardware, cloud platforms, and IT services. It also offers solutions for AI, machine learning, hybrid cloud, and cybersecurity. The company historically funded its growth through public markets but was taken private by Michael Dell and Silver Lake in 2013, only to return to public markets in 2018 after the EMC merger.
Key competitors include HP Inc., Lenovo, Apple, Cisco, NetApp, IBM, and HPE (Hewlett Packard Enterprise), depending on the product segment. In PCs, Dell competes heavily with HP, Lenovo, and Apple; in servers and enterprise storage, it goes head-to-head with HPE, Cisco, and NetApp.
Headquarters and Global Presence
Dell Technologies is headquartered in Round Rock, Texas, with major offices across the U.S., Europe, Asia, and Latin America. The company serves over 180 countries and operates significant supply chain and R&D centers globally. Its international operations make it one of the most geographically diversified technology companies.
Market Overview
Dell operates in the global IT hardware and enterprise infrastructure market, which includes PCs, servers, storage, networking, and IT services. The PC market is mature, with growth largely dependent on refresh cycles, enterprise IT upgrades, and hybrid work adoption. On the other hand, the enterprise infrastructure and cloud computing market continues to expand rapidly, fueled by demand for AI workloads, data storage, and digital transformation initiatives.
By 2030, the global IT infrastructure market is projected to exceed $2 trillion, growing at a CAGR of 6–7%. Servers optimized for AI and high-performance computing are expected to be one of the fastest-growing categories, with double-digit CAGR through 2030. This positions Dell strongly given its leadership in AI servers and enterprise solutions.
Competitor Landscape
In PCs, Dell faces stiff competition from HP and Lenovo, which often compete aggressively on price and global market share. Apple maintains a premium position with MacBooks, commanding higher margins. In enterprise infrastructure, HPE, Cisco, and IBM are Dell’s biggest rivals, each with strong data center and cloud offerings.
Unique Differentiation
Dell’s differentiation lies in its end-to-end IT solutions, spanning from consumer laptops to enterprise-grade servers, storage, and cloud platforms. Its ability to bundle hardware, software, and services into integrated solutions for enterprises makes it a one-stop shop for IT modernization. Dell’s direct-sales heritage, strong enterprise relationships, and AI-optimized server portfolio provide a unique competitive edge.
Management Team
- Michael Dell (Founder, Chairman & CEO) – Founder since 1984, Michael Dell has been the visionary behind Dell’s transformation from a PC maker to a diversified enterprise technology leader.
- Jeff Clarke (Vice Chairman & Co-COO) – Oversees global operations, technology development, and product innovation. Clarke has been instrumental in Dell’s infrastructure business growth.
- Yvonne McGill (CFO) – Responsible for finance, accounting, and investor relations. She has played a key role in cost management and strategic capital allocation.
Financial Performance (Last 5 Years)
Over the last five years, Dell has delivered steady revenue growth. In FY2020, revenue was $92 billion, and by FY2025, revenue had grown to nearly $96 billion, reflecting a modest CAGR of ~1%. The pandemic initially boosted PC sales, but post-2022 growth was driven by infrastructure solutions.
Earnings grew faster than revenue, with net income rising from $4.6 billion in FY2020 to $7.8 billion in FY2025, a CAGR of around 11%. This improvement was driven by higher-margin enterprise sales and operational efficiency. Dell has also reduced its debt significantly since the EMC merger, strengthening its balance sheet.
Cash flow from operations has consistently exceeded $8 billion annually, allowing Dell to invest in R&D, reduce debt, and return capital to shareholders through dividends and buybacks. The balance sheet today is much stronger, with net debt significantly reduced.
Bull Case for Dell Stock
- Strong enterprise demand for AI-optimized servers and infrastructure solutions.
- Diversification beyond PCs into high-margin infrastructure and cloud solutions.
- Healthy balance sheet with strong free cash flow supporting shareholder returns.
Bear Case for Dell Stock
- PC market stagnation may limit overall revenue growth.
- Heavy competition in servers and enterprise IT could pressure margins.
- Exposure to global supply chain risks and cyclical IT spending cycles.
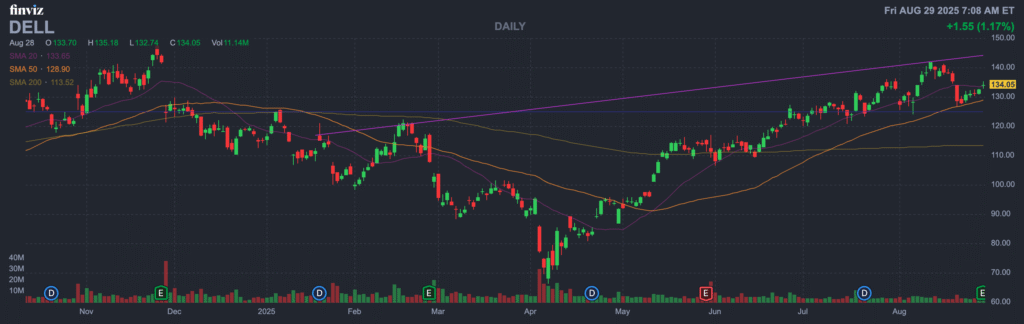
The stock is in a stage 2 markup on the monthly and weekly charts, and is on a stage 3 consolidation (bearish) on the daily chart. The near term move is to the $120 range, where it should reverse, but has also downside to the $109 range.