Executive Summary:
United Parcel Service (UPS) is a global logistics leader, primarily known for its worldwide package delivery services. Founded in 1907, UPS has evolved from a messenger company to a multinational corporation offering a wide range of supply chain solutions. The company’s operations encompass transportation, logistics, and related services, utilizing an extensive network of ground and air transportation.

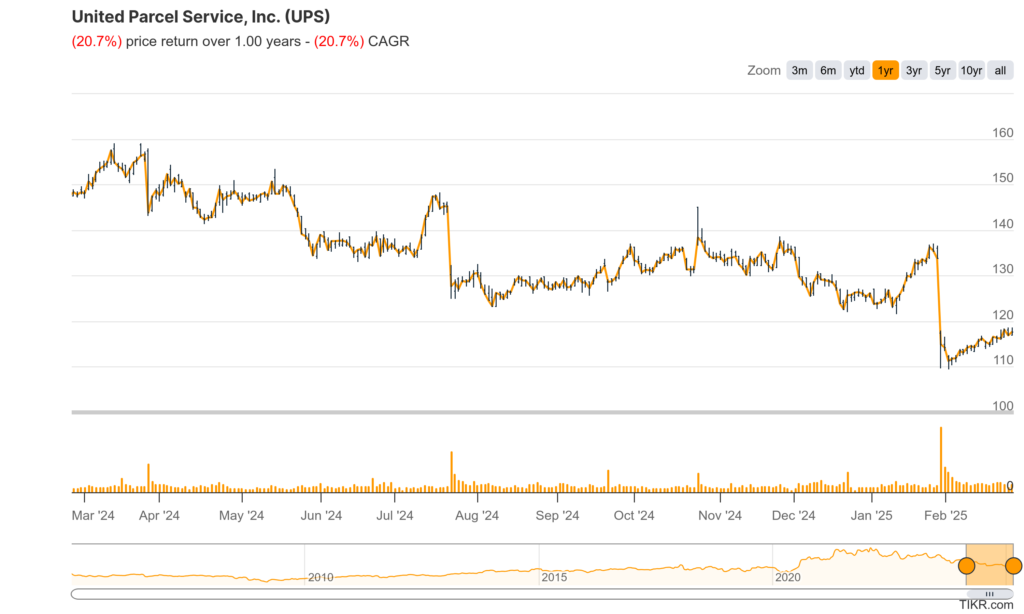
UPS reported consolidated revenues of $25.3 billion, a 1.5% increase from the fourth quarter of 2023. Diluted EPS was $2.01, while non-GAAP adjusted diluted EPS reached $2.75, which was above analyst expectations.
Stock Overview:
| Ticker | $UPS | Price | $117.63 | Market Cap | $100.48B |
| 52 Week High | $158.95 | 52 Week Low | $109.40 | Shares outstanding | 739.87M |
Company background:
United Parcel Service Inc. (UPS) is a globally recognized logistics and package delivery company with a rich history. It was founded in 1907 in Seattle, Washington, by James E. Casey and Claude Ryan, initially as the American Messenger Company. The company’s core mission was to provide reliable messenger services, and it gradually evolved into a package delivery giant. UPS expanded its services and geographical reach, becoming a cornerstone of global commerce.

UPS offers a comprehensive suite of logistics solutions, including package delivery, freight transportation, and supply chain management. Their products and services encompass:
- Package Delivery: Ground and air delivery services for domestic and international shipments.
- Freight Services: Less-than-truckload (LTL) and truckload freight transportation.
- Supply Chain Solutions: Warehousing, distribution, and logistics management.
- Specialized Services: Including services for healthcare logistics, e-commerce, and returns.
UPS faces strong competition from other major players in the logistics industry. Key competitors include FedEx, DHL, and the United States Postal Service (USPS). These companies compete on factors such as delivery speed, service reliability, and pricing.
UPS is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. This location serves as the central hub for the company’s global operations. UPS has played a vital role in facilitating the movement of goods around the world.
Recent Earnings:
Revenue and Growth: UPS reported fourth-quarter 2024 consolidated revenues of $25.3 billion. This represents a 1.5% increase compared to the fourth quarter of 2023.
EPS and Growth: Diluted earnings per share (EPS) were $2.01. Non-GAAP adjusted diluted EPS reached $2.75, showing growth compared to the previous year.
UPS is implementing strategic changes, including adjustments to its relationship with its largest customer and efficiency initiatives. For 2025, UPS provided forward guidance, projecting consolidated revenue of approximately $89.0 billion. There are also changes to their relationship with their largest customer, and efficiency initiatives that the company is undertaking.
The Market, Industry, and Competitors:
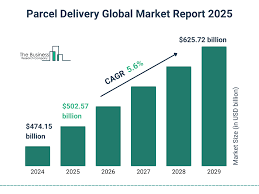
UPS operates within the global logistics and package delivery market, a sector heavily influenced by e-commerce growth, international trade, and evolving supply chain demands. This market is characterized by intense competition among major players like FedEx, DHL, and regional carriers. The rise of online shopping has significantly driven demand for package delivery services, particularly for last-mile delivery. The increasing complexity of global supply chains has created opportunities for logistics providers to offer comprehensive solutions, including warehousing, distribution, and freight forwarding. The market is also seeing a surge in demand for specialized services, such as cold chain logistics for pharmaceuticals and time-sensitive deliveries.
The global logistics market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by the ongoing expansion of e-commerce and the need for efficient supply chain solutions. Predictions indicate a significant increase in parcel volumes, especially in emerging markets. Analysts project a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) in the mid-single digits (e.g., 5-7%) for the logistics market through 2030. This growth will be fueled by technological advancements, such as automation and data analytics, which are improving operational efficiency and enabling more precise delivery services. UPS, with its extensive network and established infrastructure, is positioned to capitalize on these growth opportunities, while also adapting to the changing demands of the market.
Unique differentiation:
FedEx: FedEx is arguably UPS’s most direct and significant competitor. Like UPS, FedEx offers a wide range of shipping and logistics services, including express delivery, ground shipping, and freight services. They compete fiercely for market share in both domestic and international markets. FedEx is known for its strong air delivery network.
DHL: DHL is a global logistics giant, particularly strong in international shipping. It’s a division of Deutsche Post DHL Group. DHL is making it a major competitor for UPS in global shipping and logistics solutions.
United States Postal Service (USPS): The USPS is a major competitor in the domestic market, particularly for smaller packages and residential deliveries. The USPS offers a wide range of services at competitive prices, especially for ground shipping.
Other Competitors: UPS also competes with other logistics providers: XPO Logistics, C.H. Robinson, Amazon Logistics, which is increasingly becoming a very large competitor.

Extensive Integrated Network: UPS boasts one of the most comprehensive and integrated logistics networks globally. This allows them to efficiently handle a vast volume of packages across diverse transportation modes, including ground and air. This integrated network creates a very efficient system.
Strong Ground Operations: UPS is particularly recognized for its robust ground delivery network, especially within the United States. This strength in ground operations provides a reliable and cost-effective solution for a large segment of its customer base.
Focus on Comprehensive Solutions: UPS offers a broad range of logistics services beyond basic package delivery, including supply chain solutions, freight services, and specialized services for industries like healthcare. This comprehensive approach allows them to cater to diverse customer needs.
Management & Employees:
Carol B. Tomé: Serves as the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of UPS.
Nando Cesarone: EVP & President U.S.
Kate Gutmann: EVP & President International, Healthcare and Supply Chain Solutions.
Bala Subramanian: EVP & Chief Digital and Technology Officer.
Financials:
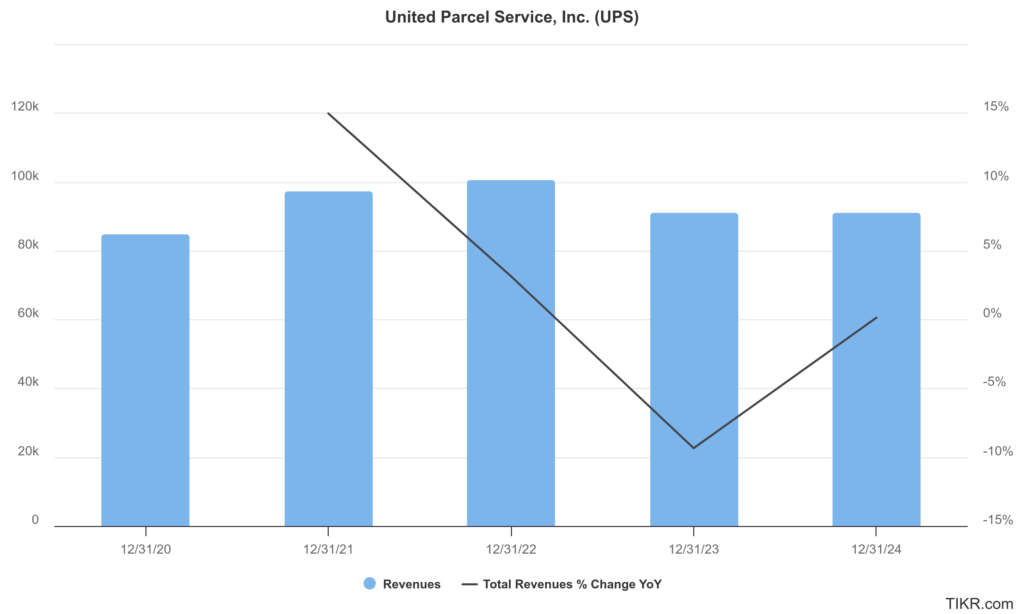
United Parcel Service Inc. (UPS) has reported a revenue of $91.1 billion, marking a significant milestone in its financial performance. The revenue growth has not been consistent across all segments. The U.S. Domestic Segment has seen steady growth, while the International Segment has also contributed positively, with revenue increases driven by volume growth.
The company’s net income has been impacted by various factors, including pension adjustments and strategic initiatives. UPS has maintained a strong operational performance, with operating profits increasing in recent quarters. For example, in Q4 2024, the operating profit rose by 18.1% compared to the previous year. The earnings per share (EPS) have also shown resilience, with non-GAAP adjusted EPS often exceeding analyst expectations.
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for UPS’s revenue over the past few years has been influenced by market conditions and strategic decisions. UPS has generally experienced growth in service revenue across its segments. The company’s strategic initiatives and efficiency programs aim to enhance profitability and competitiveness in the market.
The company has utilized debt financing to support capital asset expansions and discretionary payments to pension plans. Cash from operations has been a source of funding for these initiatives. UPS generated $10.1 billion in cash from operations and returned $5.9 billion to shareholders through dividends and share repurchases. This financial management strategy reflects UPS’s focus on maintaining a strong financial foundation while investing in growth opportunities.

Technical Analysis:
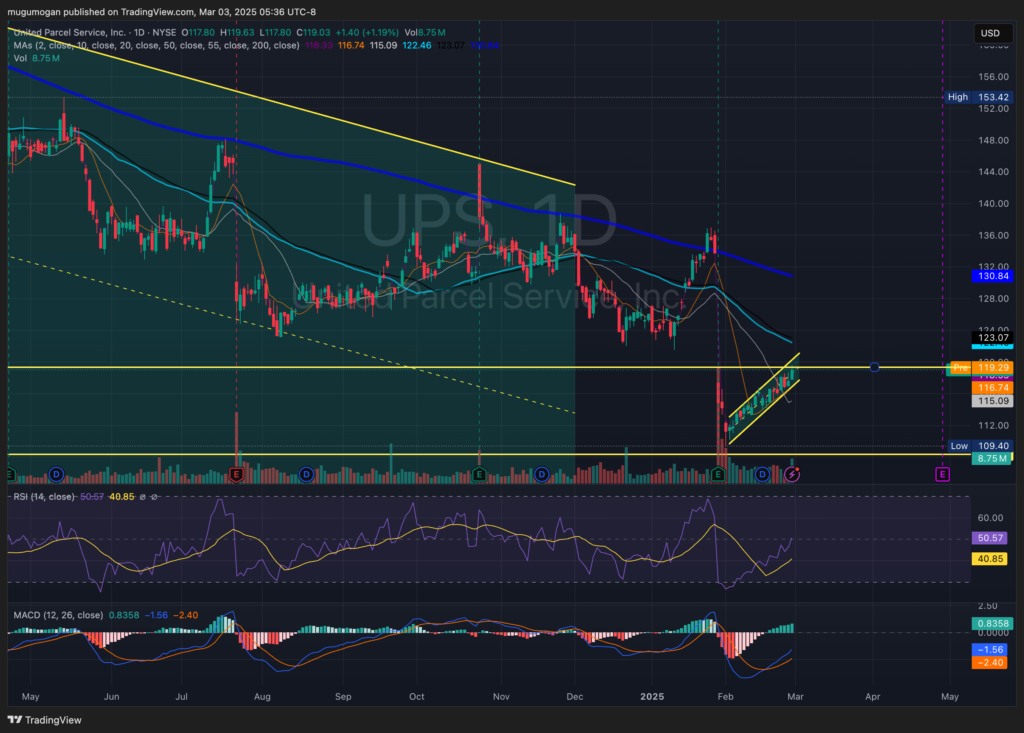
The stock is in a stage 4 decline on the monthly chart (Bearish) and has a bear flag on the weekly chart (Bearish). There is an attempted reversal into the gap on the daily chart, where it has some resistance in the $$120 zone, but this should fall again to the $108 zone. If it does get into the gap it would be a good entry for a medium term swing position.
Bull Case:
Operational Efficiency and Cost-Cutting: UPS has been actively pursuing initiatives to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs, including network optimization and technology investments. Successful execution of these plans could lead to higher profit margins.
Focus on Profitable Segments: UPS is strategically focusing on higher-margin segments, such as healthcare logistics and small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). This shift could enhance profitability and drive growth.
Strategic Adaptations: The company is actively working to adapt to the changing relationship with its largest customer, and to implement efficiency initiatives. If these adaptations are successful, this will improve the companies bottom line.
Bear Case:
Intense Competition: The logistics industry is highly competitive, with major players like FedEx, DHL, and Amazon Logistics vying for market share. Price wars and increased competition could pressure profit margins.
Labor Costs and Negotiations: UPS has a large workforce, and labor costs are a significant expense. Potential labor disputes or rising labor costs could impact profitability.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions: Ongoing global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, or trade disputes could negatively impact international shipping volumes and create operational challenges.
