Executive Summary:
McDonald’s Corporation is a globally recognized fast-food giant, originating as a small restaurant. It has evolved into a multinational corporation, famous for its iconic hamburgers, fries, and widespread franchise model. The company’s business model relies on revenue from both company-operated restaurants and franchise fees.

McDonald’s Corporation reported earnings per share (EPS) was $2.83, while analysts had forecasted $2.90. The company’s revenue for the quarter came in at $6.39 billion, falling short of the anticipated $6.51 billion.
Stock Overview:
| Ticker | $MCD | Price | $307.91 | Market Cap | $220.18B |
| 52 Week High | $326.32 | 52 Week Low | $243.53 | Shares outstanding | 715.07M |

Company background:
McDonald’s Corporation was founded in 1940 as a restaurant operated by brothers Richard and Maurice McDonald in San Bernardino, California. Initially, it was a drive-in restaurant, but they later revolutionized their operations by implementing the “Speedee Service System” in 1948, which streamlined food preparation and service, focusing on a limited menu. Ray Kroc, a milkshake machine salesman, was impressed by their efficiency and envisioned the potential for a nationwide chain. He joined the company as a franchise agent in 1955 and subsequently purchased the business from the McDonald brothers in 1961 for $2.7 million. The initial funding for expansion came from Kroc’s own resources and subsequent franchise fees.

McDonald’s core product offerings have historically centered on hamburgers, particularly the Big Mac, Quarter Pounder, and cheeseburgers. They also feature Chicken McNuggets, French fries, various breakfast items (including the Egg McMuffin), salads, desserts, and beverages. The menu has adapted to regional tastes and dietary trends, introducing items like McSpicy chicken sandwiches and plant-based options in certain markets.
Key competitors include other fast-food giants such as Burger King (Restaurant Brands International), Wendy’s, and Yum! Brands (which owns KFC and Taco Bell). These companies compete for market share by offering similar products, promotional strategies, and customer loyalty programs. McDonald’s faces competition from fast-casual restaurants like Chipotle and Panera Bread, which cater to consumers seeking higher-quality ingredients and customizable options. The competitive landscape also includes local and regional fast-food chains, as well as emerging food delivery services that impact traditional restaurant dining.
McDonald’s Corporation’s headquarters are located in Chicago, Illinois. The move to Chicago in 2018 from Oak Brook, Illinois, signified a strategic shift to attract talent and foster innovation in a more urban environment.
Recent Earnings:
McDonald’s Corporation reported revenue of $6.39 billion, which was below the analysts’ anticipated $6.51 billion. The earnings per share (EPS) was $2.83, also lower than the projected $2.90.
Despite the revenue and EPS misses, McDonald’s global comparable sales showed a modest increase in the fourth quarter. McDonald’s is emphasizing growth through digital and loyalty programs, which are seeing increases in users and sales. The company is also planning on significant expansion, with plans to open a large number of new restaurants in the coming years.
McDonald’s has outlined plans for continued investment in its digital platforms and loyalty programs. They have also published plans for the expansion of new restaurants.
The Market, Industry, and Competitors:
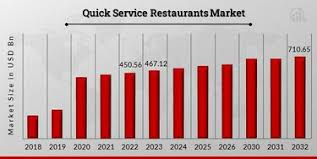
McDonald’s Corporation operates within the global quick-service restaurant (QSR) market, a highly competitive sector characterized by intense rivalry among established chains and emerging fast-casual concepts. This market is driven by factors such as convenience, affordability, and evolving consumer preferences. McDonald’s, as a dominant player, navigates this landscape by leveraging its brand recognition, extensive global footprint, and continuous menu innovation. The QSR market is also increasingly influenced by digital trends, including online ordering, delivery services, and loyalty programs, which McDonald’s actively integrates into its operations. Additionally, changing dietary preferences and health consciousness are prompting the company to diversify its offerings and emphasize sustainability.
The global QSR market is expected to experience steady growth, driven by increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes in emerging economies, and the continued demand for convenient food options. Projections indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 4-5% through 2030, though precise figures vary depending on regional factors and market research. McDonald’s, with its substantial resources and global reach, is well-positioned to capitalize on this growth. To achieve this, McDonald’s is focusing on strategic expansion, particularly in high-growth markets, and enhancing its digital capabilities to improve customer experience and drive sales. The company is also adapting its menu to cater to evolving consumer preferences, including healthier options and plant-based alternatives, to remain competitive in the long term.
Unique differentiation:
McDonald’s Corporation faces intense competition within the global quick-service restaurant (QSR) market. Its primary competitors include other major fast-food chains like Burger King, owned by Restaurant Brands International, which offers a similar menu of burgers, fries, and other fast-food items. Wendy’s, another significant player, competes directly with its focus on fresh, never-frozen beef and a broader menu of sandwiches and sides. Yum! Brands, the parent company of KFC and Taco Bell, also poses a substantial competitive threat, offering distinct menu options that cater to diverse consumer preferences. These competitors vie for market share through similar strategies, including aggressive pricing, promotional campaigns, and extensive advertising, all aimed at attracting and retaining customers.
Chains like Chipotle Mexican Grill and Panera Bread offer higher-quality ingredients and customizable options, appealing to consumers seeking a more premium dining experience. The rise of food delivery services and online ordering platforms has intensified competition, as consumers have access to a wider range of dining options with greater convenience. Local and regional fast-food chains also present competitive challenges, often catering to specific regional tastes and preferences.

Global Brand Recognition and Scale: McDonald’s possesses unparalleled global brand recognition. Its iconic “Golden Arches” are universally recognized, providing a significant advantage in attracting customers worldwide. The sheer scale of its operations, with thousands of restaurants across numerous countries, allows for economies of scale in sourcing, distribution, and marketing, contributing to cost leadership.
Adaptability and Localization: While maintaining core menu items, McDonald’s demonstrates a strong ability to adapt its offerings to local tastes and preferences. This localization strategy allows it to cater to diverse cultural and dietary needs, expanding its market reach. This can be seen in the various regional food offerings that differ from country to country.
Real Estate Portfolio: A significant and often overlooked aspect of McDonald’s differentiation is its substantial real estate portfolio. The company often owns the land and buildings of its restaurants, providing a stable revenue stream and strategic control over prime locations.
Management & Employees:
Chris Kempczinski: He serves as the President, Chairman, and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of McDonald’s Corporation. He holds a very important leadership role, and is responsible for the overall strategy and direction of the company.
Ian Borden: He is the Executive Vice President and Global Chief Financial Officer (CFO). In this role, he is responsible for the company’s financial management.
Gillian McDonald: She is the Executive Vice President and President of International Operated Markets. This position is responsible for the operations of company operated markets outside of the United States.
Financials:

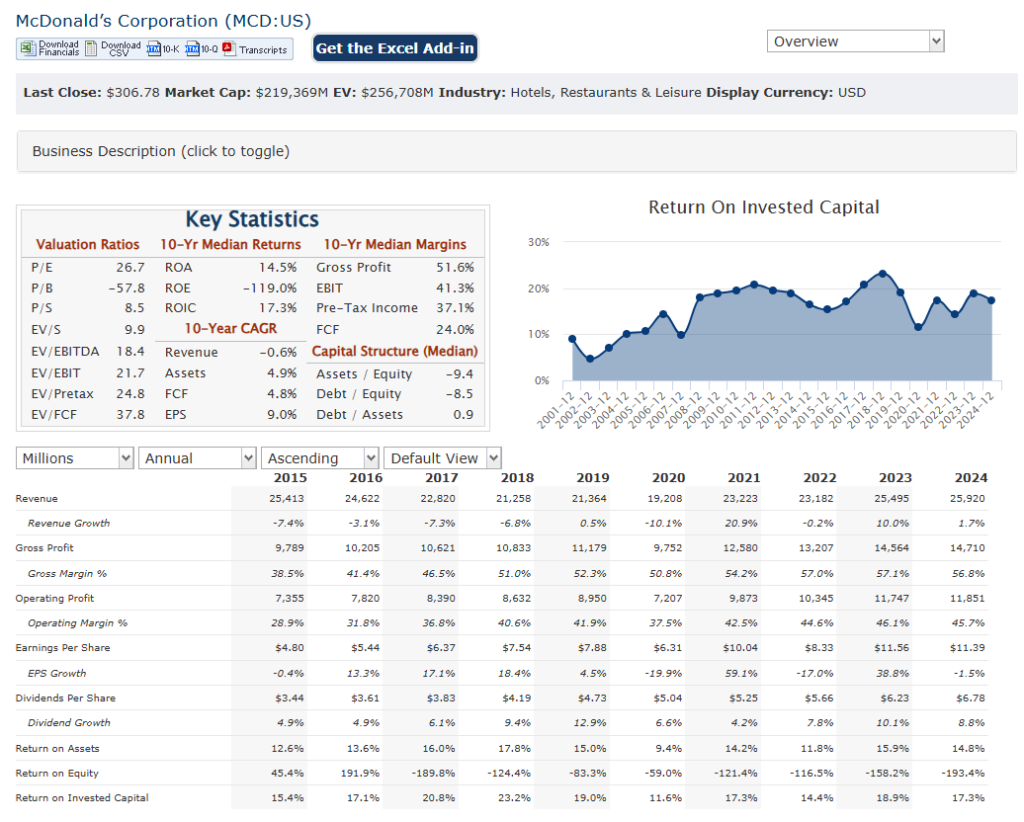
McDonald’s Corporation has net sales have shown a general upward trend, increasing from $19,208 million in 2020 to $26,549 million in 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.5%. This growth is largely attributed to strategic initiatives like menu innovations and enhanced customer loyalty programs. McDonald’s reported significant growth in systemwide sales, which exceeded $130 billion in 2024, with a notable increase in sales to loyalty members.
McDonald’s has also experienced growth, with net income rising from $4,730 million in 2020 to $8,774 million in 2025, indicating a CAGR of about 7.5%. The company’s earnings before tax (EBT) have similarly increased, from $6,141 million in 2020 to $11,095 million in 2025, reflecting a strong operational performance.
Total debt has been around $37 billion in recent years, with shareholders’ equity showing fluctuations due to various financial transactions and market conditions. McDonald’s continues to prioritize cash flow management, ensuring sufficient liquidity for operational needs and dividend payments.
The company’s strategic focus on customer value, menu innovation, and culturally relevant marketing has been key to its financial performance. McDonald’s has seen growth in international segments and loyalty programs, contributing to its overall financial resilience.
Technical Analysis:
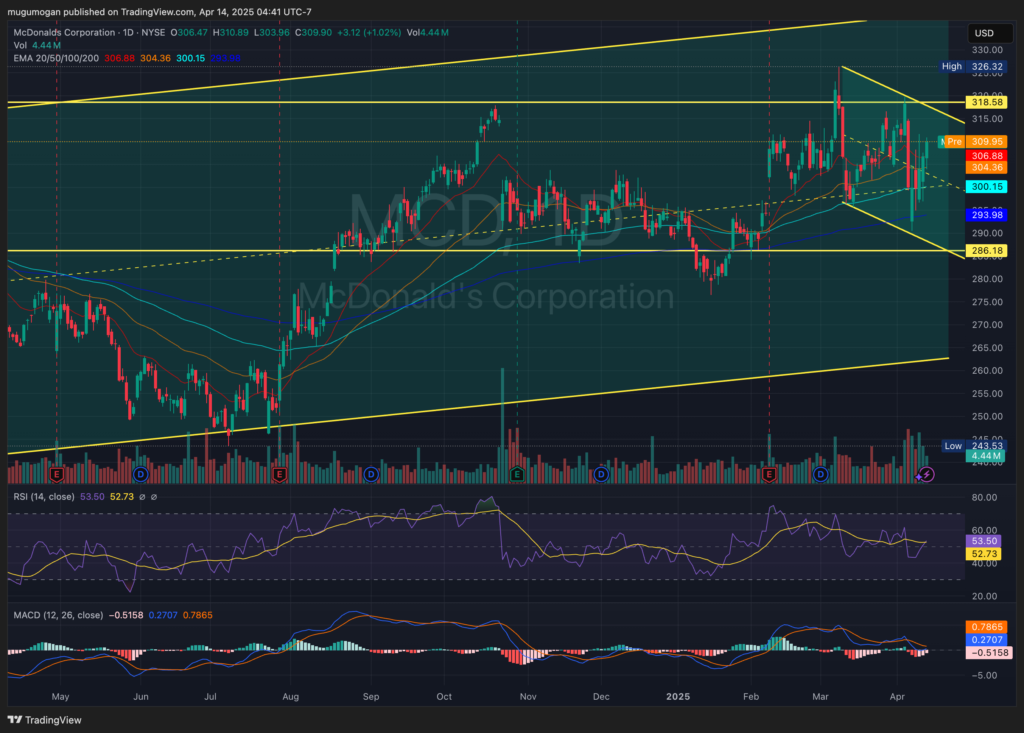
The stock is in a stage 2 bullish markup on the monthly chart and is consolidating on the weekly chart, stage 3. The daily chart is bearish with a move to the $290 range most likely in the short term.
Bull Case:
Digital Transformation and Innovation: McDonald’s is heavily investing in digital technologies, including mobile ordering, delivery services, and loyalty programs. These initiatives enhance customer experience and drive sales growth. Ongoing menu innovation and adaptation to changing consumer preferences, such as healthier options and plant-based alternatives, also contribute to growth.
Resilience in Economic Downturns: McDonald’s has historically demonstrated resilience during economic downturns. Its affordable menu options tend to attract customers seeking value, making it a relatively stable investment. This ability to retain customers during hard economic times, makes it a strong potential stock.
Bear Case:
Competition and Market Saturation: The fast-food industry is highly competitive, with established rivals and emerging fast-casual chains vying for market share. Concerns exist about market saturation in developed countries, limiting potential growth.
Currency Fluctuations: As a global company, McDonald’s is exposed to currency fluctuations, which can impact its financial results. Unfavorable exchange rates could reduce reported earnings.
Increased competition from food delivery services: While McDonald’s uses these services, they also are competition, and can decrease the amount of in store customers.