Executive Summary:
Robinhood Markets Inc. is an American financial services company that offers a commission-free trading platform accessible through a mobile app. It allows users to trade stocks, ETFs, and cryptocurrencies, and also provides cryptocurrency wallets, credit cards, and other banking services. The company generates revenue primarily through payment for order flow, net interest income, and subscription fees.

Robinhood Markets Inc. reported its revenue surged 41.5% year-over-year to $624 million. Earnings per share (EPS) of $0.18.
Stock Overview:
| Ticker | $HOOD | Price | $21.20 | Market Cap | $18.63B |
| 52 Week High | $24.88 | 52 Week Low | $7.91 | Shares outstanding | 754.86M |
Company background:
Robinhood Markets Inc. is a financial technology company that has disrupted the traditional brokerage industry. Founded in 2013 by Vlad Tenev and Baiju Bhatt. Its headquarters are located in Menlo Park, California. Initially bootstrapped, Robinhood quickly gained traction and secured substantial funding from venture capital firms, including Sequoia Capital, Andreessen Horowitz, and Ribbit Capital.
Robinhood’s core product is its mobile app, which provides a user-friendly platform for investors of all levels. Robinhood has expanded its services to include margin lending, retirement accounts, and fractional share investing, further broadening its appeal to a diverse customer base.
Recent Earnings:
Robinhood Markets Inc. reported a remarkable 40% year-over-year revenue growth, reaching $618 million. This surge was primarily driven by a 59% increase in transaction-based revenues, particularly in cryptocurrencies and options trading. The net interest revenues climbed 22% due to higher interest-earning assets and elevated short-term interest rates.
Net income surged to $157 million, translating to an EPS of $0.18, a stark contrast to the net loss. This strong performance exceeded analysts’ expectations, demonstrating Robinhood’s ability to capitalize on favorable market conditions and enhance its operational efficiency.
Net deposits reached a record high, indicating strong customer inflow. Gold subscribers, a key indicator of engagement, also grew substantially.
The Market, Industry, and Competitors:
Robinhood operates in the highly competitive and rapidly evolving financial technology (fintech) industry, specifically within the retail brokerage segment. The market has witnessed significant disruption with the rise of commission-free trading platforms and a growing emphasis on user experience and accessibility. Robinhood has successfully tapped into the millennial and Gen Z demographic, offering a mobile-first approach to investing.
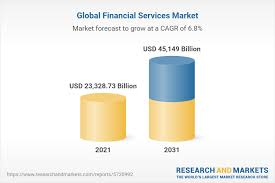
The fintech industry is projected to experience substantial growth, driven by factors such as increasing smartphone penetration, rising disposable incomes, and a growing interest in financial literacy. This growth is expected to positively impact the retail brokerage market, including Robinhood’s operations.
As Robinhood continues to innovate and expand its product offerings, it has the potential to outperform the industry average, contributing to a higher CAGR for the company.
Unique differentiation:
Robinhood operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, with a range of established financial institutions and emerging fintech startups vying for market share. Traditional brokerages like Charles Schwab, E*TRADE, and TD Ameritrade pose significant competition, offering a broader suite of investment products, robust research tools, and established brand recognition. These firms have been investing heavily in technology to enhance their digital offerings and attract younger investors.
Fintech competitors has emerged, targeting specific niches or offering unique value propositions. These include commission-free rivals like Webull and Interactive Brokers, which compete on features, pricing, and platform capabilities. Other players like Public.com and Stash focus on social investing and automated investing, respectively. To maintain its competitive edge, Robinhood must continually innovate and differentiate its platform while addressing concerns around user experience and financial education.

Robinhood’s primary differentiation lies in its focus on simplicity, accessibility, and a mobile-first approach to investing. Unlike traditional brokerages with complex platforms and high minimum balances, Robinhood has built a user-friendly app that caters to a younger demographic new to investing. By eliminating commission fees, Robinhood lowered the barrier to entry for millions of people, democratizing access to the stock market.
Robinhood’s gamification elements, such as fractional share investing and easy-to-understand charts, have helped to make investing more engaging and less intimidating for novice traders. While the company has faced criticism for its role in fueling speculative trading, its core value proposition of providing a straightforward platform for retail investors.
Management & Employees:
Vlad Tenev is the Co-Founder, Chief Executive Officer (CEO), and President of Robinhood Markets Inc. He also serves as the Chair of the board of directors. Tenev co-founded Robinhood with Baiju Bhatt in 2013.
Baiju Bhatt is a Co-Founder of Robinhood and served as a member of the board of directors since the company’s inception. He co-founded Robinhood with Vlad Tenev in 2013 and served as Co-CEO and Co-President until November 2020. He held the position of Chief Creative Officer until March 2024.
Financials:
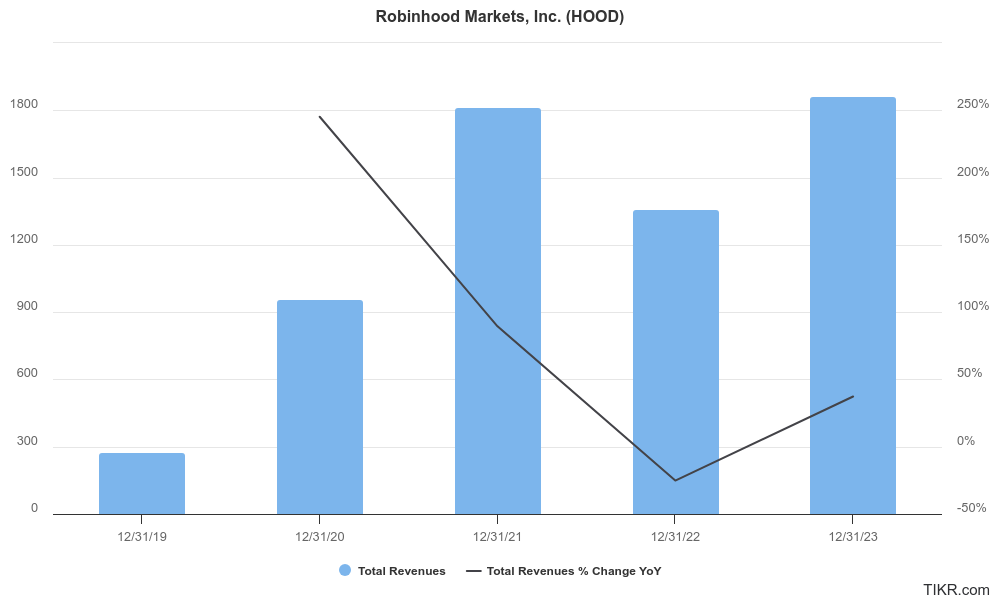
Early Years and Revenue Growth: The company’s commission-free trading model attracted a large millennial and Gen Z user base. Between 2019 and 2021, revenue grew at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) exceeding 200%, fueled by a surge in trading activity and an increase in crypto transactions.
Profitability and Earnings Growth: Robinhood’s path to profitability was initially unclear. The company relied heavily on transaction-based revenue streams and faced challenges in monetizing its large user base.Earnings growth (Net Income) during this period surpassed 100% CAGR.
Balance Sheet: Cash and cash equivalents likely form a significant portion of the asset base, reflecting user deposits and potential upcoming product launches. The company’s liabilities are likely dominated by customer deposits and outstanding margin loans.
Looking Ahead: Maintaining user growth and engagement will be crucial. Expanding the product suite with new features and services like retirement accounts can diversify revenue streams. The company also needs to navigate a competitive landscape and potential regulatory changes.

Technical Analysis:
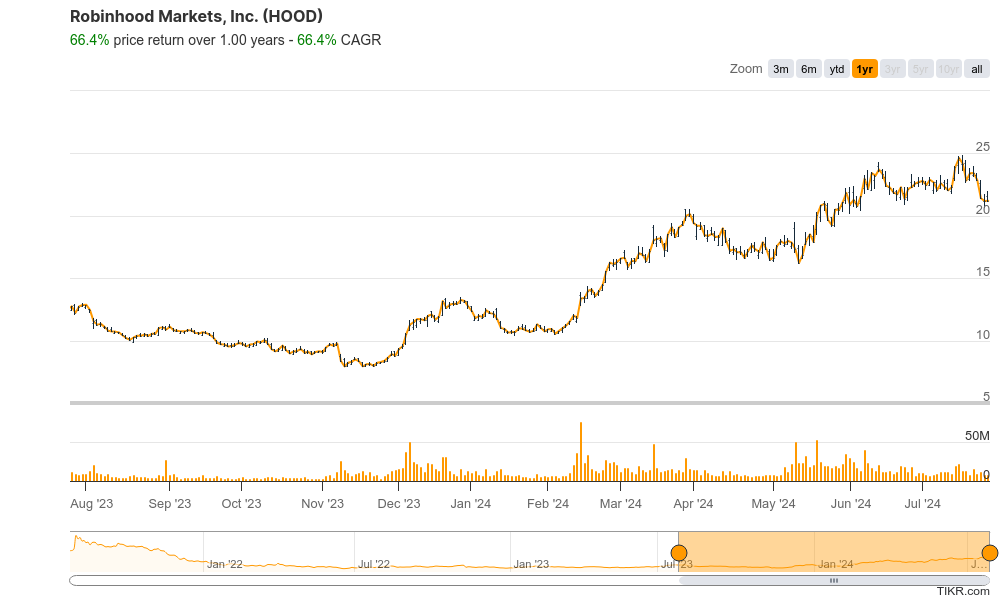
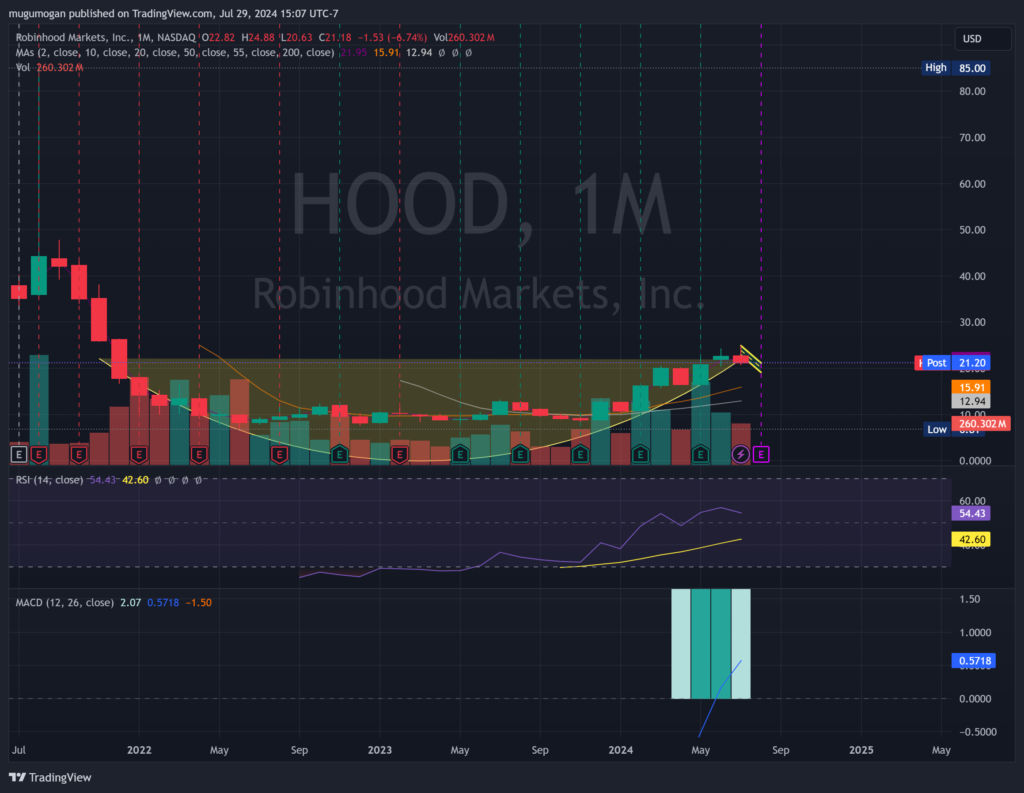
The stock has built a good base over the last 3 years since going down to the $8 range after IPO. On the monthly chart, it is consolidating on the base, and seems to want to move to stage 3 (neutral), in the $20 to $22 range. On the weekly chart, it is in stage 4 (decline, bearish) and on the daily chart it is bearish as well. There is some support in the $20 zone, but more likely in the $18 zone.
Bull Case:
Market Penetration: Robinhood has successfully tapped into a younger demographic that was previously underserved by traditional brokerages. There’s significant potential to deepen penetration within this market and expand to other demographics.
Product Expansion: The company’s move beyond commission-free trading, with offerings like cash management, crypto wallets, and retirement accounts, broadens its revenue streams and customer stickiness.
Technological Innovation: Robinhood’s user-friendly interface and focus on technology can drive customer acquisition and retention. Continued investment in technology could lead to new features and services that differentiate the platform.
Bear Case:
Revenue Concentration: Robinhood’s revenue is heavily concentrated in transaction-based fees, particularly in volatile assets like options and cryptocurrencies. A decline in trading activity or regulatory changes in these areas could significantly impact revenue.
Customer Acquisition Costs: Acquiring new users can be expensive, and maintaining user engagement is challenging. If Robinhood fails to effectively monetize its user base, profitability could be impacted.
Profitability: While Robinhood has made strides towards profitability, achieving sustained profitability remains a challenge. The company needs to effectively manage costs and increase revenue to generate consistent profits.