Company Overview: Ferrari N.V. (Ticker: RACE)
Ferrari N.V. is an Italian luxury sports-car manufacturer known globally for its iconic “Prancing Horse” emblem and racing heritage. Founded with motorsport roots in Maranello, Italy, the company now designs, engineers, produces and sells high-end performance road and track-oriented vehicles, and provides related services and licensing of its brand. The firm emphasizes exclusivity, craftsmanship, premium pricing, and limited production—all contributing to a unique luxury positioning. Its product range spans one‐off bespoke models, supercars, track-only variants and an expanding lifestyle & licensing business. Operating globally, Ferrari emphasises its dual identity of track/performance heritage and luxury brand appeal.
Recent Earnings Summary
In Q2 2025, Ferrari reported adjusted EBITDA of €709 million, up ~5.9% year-over-year, with an EBITDA margin of 39.7%. Operating profit (EBIT) reached €552 million, up ~8.1% from the prior year, with a margin of 30.9%. For the trailing-twelve-months revenue rose ~9.3% to about €6.96 billion. The company has also raised its guidance: it expects 2025 net revenues of at least €7.1 billion and has set a longer-term target of about €9 billion by 2030. Although the precise EPS for Q2 was not detailed here, the consistent margin expansion and revenue growth signify healthy underlying momentum.
Founding, Products, Headquarters & Competitors
Ferrari traces its origins to Enzo Ferrari, with the company’s first car built under the Ferrari marque in 1947 in Maranello, Italy. Headquarters remain in Maranello, Emilia-Romagna region, Italy. The company went public on the NYSE on October 21, 2015. Ferrari’s product lineup spans high-performance road cars, limited-edition one-offs (for high-net-worth clients), track-only variants, and related accessories/licensing (e.g., brand apparel, lifestyle). The business also offers after-sales, maintenance, restoration, and historic programmes. Key competitors include other ultra-luxury and performance car manufacturers such as Lamborghini S.p.A., Porsche AG, Aston Martin Lagonda Global Holdings pic, and more broadly premium auto groups like Mercedes‑Benz Group (via AMG) and BMW AG (via M). Ferrari competes not just on car performance, but brand aura, exclusivity, and margin.
Market & Growth Expectations
Ferrari operates in the global luxury performance automobile market—where demand is driven by high-net-worth individuals, brand desirability, limited supply, bespoke customisation, and global expansion (particularly in North America, the Middle East and Asia). The broader luxury car market is expected to grow steadily over the next decade, supported by global wealth growth, emerging market participation, and increasing appetite for premium experiences. Ferrari’s specific guidance targets revenue of ~€9 billion by 2030, up from ~€6.7–7.0 billion today, implying a CAGR roughly in the low to mid-single digits (depending on base year) to 2030. The company also benefits from margin expansion potential through higher customisation, limited edition models, brand licensing, and electric/hybrid vehicle introduction. Ferrari’s low exposure to economically sensitive markets (such as China) and limited volume strategy help protect margins during macro headwinds.
Competitor Overview
Among Ferrari’s competitors, some key contrasts: Lamborghini emphasises raw, extreme performance and flamboyant styling; Porsche mixes performance with broader volume and technical innovations (including EVs); Aston Martin provides limited-production luxury GTs with a strong British heritage. Ferrari stands apart by combining racing heritage (especially via its F1 programme), ultra-limited supply, strong brand valuations, and a focus on high margin boutique manufacturing. These competitors each face their own challenges (volume scaling, brand dilution, EV transition, margin pressure) which can create opportunity for Ferrari if it maintains brand discipline and margin focus.
Unique Differentiation
Ferrari differentiates through its heritage and exclusivity: the “Prancing Horse” brand carries almost unrivalled prestige in the luxury-sports segment. Its business model deliberately limits supply to maintain scarcity, enabling higher pricing and margin. The integration of its racing DNA with road-car production fosters strong brand emotional connection among customers and collectors. Its bespoke customisation (tailor-made programmes), high share of value from personalisation, and strong second-hand/resale value support its luxury positioning. Additionally, Ferrari’s strategy of margin over volume, combined with selective geographic exposure and growing brand licensing, gives it a structural advantage in the ultra-luxury niche.
Management Team
- Benedetto Vigna (CEO): Appointed in 2021, he leads Ferrari’s strategic transformation including electrification, customisation, and luxury brand expansion.
- John Elkann (Chairman): He represents Exor’s substantial shareholding and helps steer Ferrari’s governance and long-term vision.
- Piero Ferrari (Vice Chairman): Son of founder Enzo Ferrari, he retains both equity and a symbolic leadership role, supporting brand heritage continuity.
Financial Performance (Last 5 Years)
Ferrari has shown consistent revenue growth: for example, annual revenue in 2024 was approximately €6.68 billion with growth ~11.8% over the prior year. The trailing-twelve-months revenue as of mid-2025 is about €6.96 billion, up ~9.3% year-over-year. On the earnings side, net income in 2024 reached about US$1.647 billion (≈€1.50 billion) up ~21.5% versus 2023. The adjusted net profit has climbed steadily: in 2023 it was €1,257 million, in 2022 it was €939 million. These figures imply earnings growth CAGR in the double-digits over the recent few years. The company’s balance sheet is strong: Ferrari carries significant free cash flow, modest leverage, and healthy margins—EBITDA margin in 2024 was ~38.3%. The disciplined volume strategy and high customisation income have supported margin resilience in a global auto industry otherwise under pressure.
Bull Case
- Attractive luxury brand with high pricing power and margin resilience, making it less vulnerable to conventional auto cyclicality.
- Limited supply/controlled volume strategy + growing global wealth base (targeting new markets) offer room for growth without dilution of exclusivity.
- Electrification and brand extension (e.g., first fully-electric vehicle launch) provide a modern growth vector while maintaining luxury position.
Bear Case
- Extremely high valuation — much of the growth is already priced in; any slip in execution (EV transition, supply chain, macro) could harm sentiment.
- Increasing regulatory/technological pressure (EV mandates, emissions rules) may erode luxury petrol/diesel car segment profitability or raise cost burdens.
- Exclusivity strategy limits scale – if global luxury demand weakens or competition intensifies (from new premium EV entrants) Ferrari’s high-end niche could be more exposed.
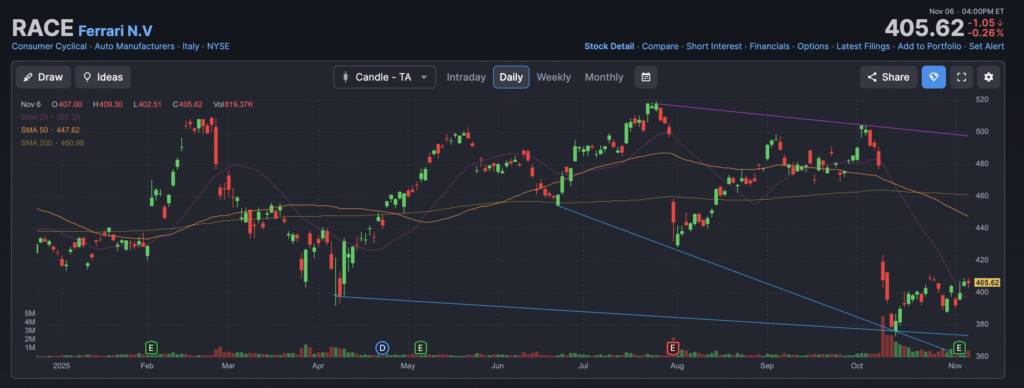
The stock is in a stage 3 neutral consolidation on the monthly and weekly charts, but is more narrowly bound in the $375 – $425 range on the daily chart. The stock should come on the top end of that zone to be interesting.