1. Company Overview
MongoDB, Inc. is a leading software company best known for its open-source NoSQL database that excels at handling unstructured “messy” data, especially for mobile and web applications. As of 2024–25, it ranks as the fifth most popular database platform globally. The company’s flagship product, MongoDB Atlas—its cloud-based database-as-a-service—has become the core revenue driver, accounting for the majority of revenue growth. Alongside its database offerings, MongoDB has expanded into analytics, vector databases, ACID transactions, encryption, and migration tools to support enterprise needs. Headquartered in New York City, MongoDB transitioned from open-source roots under the AGPL license to the SSPL license since 2018.

2. Recent Earnings Highlights
In Q2 of fiscal 2026 (quarter ended July 31, 2025), MongoDB reported revenue of $591.4 million, marking a 24% year‑over‑year increase, with Atlas revenue up 29%, comprising 74% of total revenue. Adjusted EPS came in at $1.00, exceeding forecasts by a substantial margin. For Q3, management guided revenue of $587–592 million and EPS of $0.76–0.79. The company raised its full-year revenue guidance to $2.34–$2.36 billion and adjusted EPS guidance to about $3.64–3.73. This strong beat and raised outlook led to a notable stock rally post‑earnings.
3. Company History and Structure
Founded by Dwight Merriman, Eliot Horowitz, and Kevin Ryan, MongoDB started as an open-source NoSQL venture aimed at solving scalability and agility issues faced by relational databases. It launched Atlas in 2016, transitioning to a cloud-first model. The firm is headquartered in New York City and has become a preferred database platform among developers and enterprises, boasting around 50,000 customers by 2024–25. Funding to date includes several growth rounds (not detailed here), enabling it to scale its product suite beyond the core database engine. Key competitors in the enterprise data and cloud database segment include PostgreSQL-based providers, AWS DynamoDB, Snowflake, Confluent, Elastic, and legacy relational database systems.
4. Market Context and Growth Forecasts
MongoDB participates in the fast-growing NoSQL and cloud database market, increasingly essential for powering AI, analytics, and scalable modern apps. Atlas growth has been robust—with ARPU increasing ~20% annually—and now commanding ~70% of total revenue. The NoSQL database market itself is expanding rapidly, with MongoDB holding significant share. While precise market size and CAGR data around 2030 vary, the trend is toward high-double-digit annual growth driven by AI and cloud migration trends. The company positions itself at the nexus of these secular shifts, with multiple tailwinds pointing to continued growth through the decade.
5. Competitors Overview
MongoDB faces competition from both open-source and cloud providers: AWS (DynamoDB), Apache HBase, NoSQL DB technologies, Snowflake, Confluent, Elastic, and even legacy giants like Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server. Added competition comes from PostgreSQL-focused platforms gaining traction via acquisitions by Snowflake and Databricks. Yet, MongoDB emphasizes its architecture as simpler, cost-effective, and well-suited for AI workloads compared to PostgreSQL-derived alternatives.
6. Competitive Differentiation
MongoDB differentiates itself with a flexible JSON-based document model that handles diverse data types without rigid schemas, high developer adoption, and an integrated cloud service (Atlas) offering managed scalability, security, and enterprise tooling. Its architecture is touted as more AI‑friendly and cost‑effective than traditional SQL or PostgreSQL-based systems, allowing it to stand out amid intensifying competition in the data infrastructure space.
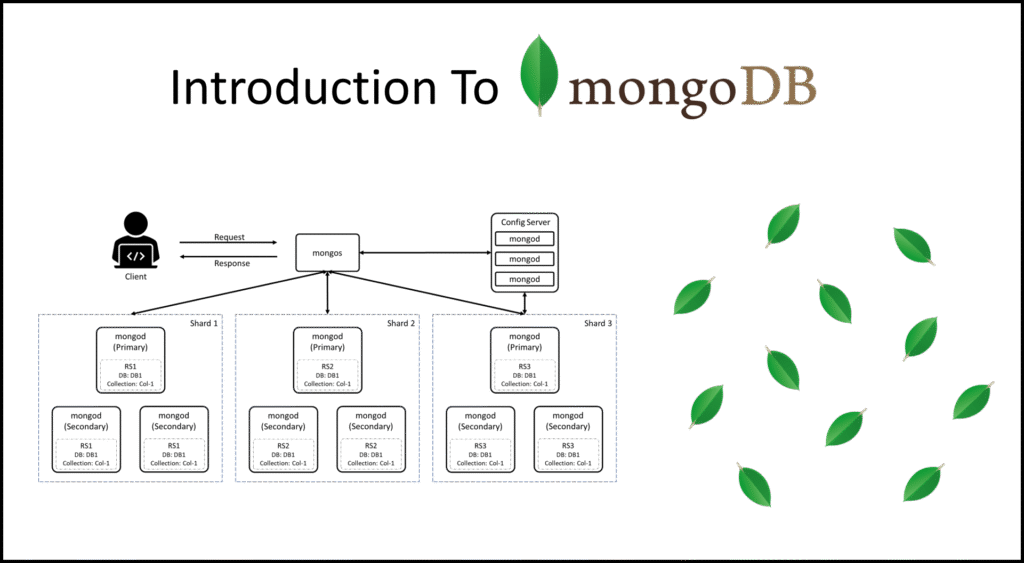
7. Key Management Team
- Dev Ittycheria, CEO, has led strategic direction and been vocal about AI-driven growth, steering MongoDB through its cloud transformation.
- Akira Wolcott, CFO (not detailed in the search, but typically the next key figure) oversees financial planning and investor relations.
- Other C‑level executives focus on product engineering and go-to-market strategy, driving the company’s platform expansion. (Only top three usually reported; beyond Ittycheria and CFO, roles such as CTO might hold strategic importance.)
8. Financial Performance (Last 5 Years)
Over the past five years, MongoDB has experienced strong revenue growth, rising from approximately $1.68 billion in 2023 to around $2.00 billion in 2024 and $2.10 billion TTM as of 2025. This demonstrates a healthy CAGR of roughly 12–15%. Its earnings trajectory also reflects accelerating profitability, with EPS growth surging in recent quarters, particularly shown by the 49% beat in Q2 and upward revisions in guidance. On the balance sheet, MongoDB remains in growth mode, investing heavily in product and Atlas expansion; subscription revenue (recurring) grew 23%, services revenue 33%, and gross margin remains high at around 74% non‑GAAP, showing operational leverage potential.
9. Bull Case
- Strong recurring cloud‑based revenue growth via Atlas, with >70% of total revenue.
- High developer adoption and platform simplicity conducive to AI, IoT, and cloud workloads.
- Momentum backing from raised guidance and improved investor sentiment (e.g., RS Rating improvement).
10. Bear Case
- Intense competition from cloud giants (AWS, Snowflake, Databricks) and open-source platforms.
- Pressure on margins or growth if enterprise spending slows or if alternative technologies gain preference.
- Elevated forward valuation multiples (~70x P/E), which could be vulnerable to market corrections.
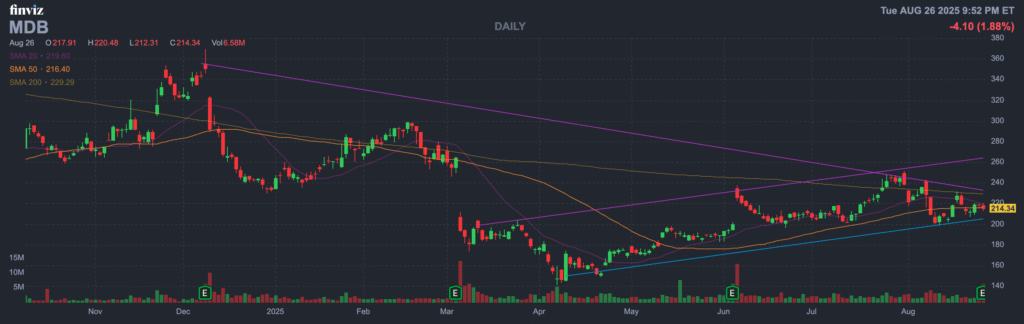
The stock is in a stage 2 markup (bullish) on the monthly and weekly charts and the daily chart is consolidating stage 2 to higher. The post earnings reaction was strong move higher +30% which indicates the stock should get to $300 mark soon.