Company Overview
Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. (NYSE: CMG) is a fast-casual restaurant chain that serves burritos, tacos, bowls, and salads made with fresh ingredients. Founded in 1993, the company popularized the “Food with Integrity” mission, prioritizing responsibly sourced ingredients and transparency. Chipotle operates over 3,500 locations, primarily in the United States, with a growing international footprint. The brand is known for its assembly-line style service and customizable meals, catering to health-conscious and convenience-driven consumers. Digital ordering, loyalty programs, and delivery partnerships have become core growth drivers post-2020.

Q2 2025 Earnings (Reported July 24, 2025)
Chipotle reported Q2 2025 earnings on July 24 with earnings per share (EPS) of $14.27, beating analyst estimates of $13.70. Revenue for the quarter reached $2.86 billion, up 14.5% year-over-year, surpassing expectations of $2.80 billion. Same-store sales grew 8.6%, driven by menu price increases and higher digital orders. Management raised full-year guidance, now projecting low-double-digit same-store sales growth and over 300 new store openings for FY25. Q3 guidance includes revenue of $2.98–$3.02 billion and EPS in the range of $14.90–$15.20.
Founding and Company Origins
Chipotle was founded in 1993 by Steve Ells, a Culinary Institute of America-trained chef, who opened the first location in Denver, Colorado. Originally intended to fund a fine dining restaurant, the success of that single burrito shop changed Ells’ trajectory. McDonald’s Corporation became an early investor in 1998, accelerating Chipotle’s expansion. The company went public in 2006, marking one of the most successful IPOs in restaurant history. Ells stepped down as CEO in 2017.
Products, Growth and Differentiators
Chipotle offers a simple menu: burritos, bowls, tacos, and salads with customizable fillings. Over time, they’ve added lifestyle bowls (Keto, Paleo, Whole30), cauliflower rice, and plant-based chorizo. The brand maintains a strong focus on clean-label food, avoiding artificial flavors, preservatives, and colors. Its in-store and mobile ordering experience is fast, scalable, and integrated with its loyalty program. The company also invested in a “Chipotlane” drive-thru digital pickup lane model to boost convenience and throughput.

Funding and Headquarters
Unlike many growth companies, Chipotle hasn’t relied on large rounds of private funding post-IPO. With a self-funding expansion model and strong free cash flow, it continues to reinvest in store openings and tech. The company is headquartered in Newport Beach, California.
Key Competitors
Major competitors include Qdoba (owned by Butterfly Equity), Taco Bell (Yum! Brands), and other fast-casuals like Sweetgreen, Shake Shack, and Panera Bread. Traditional fast food players like McDonald’s and Wendy’s also indirectly compete for wallet share in the quick dining space.
Market Landscape and Growth Outlook
Chipotle operates in the fast-casual restaurant segment, which bridges the gap between traditional fast food and full-service dining. This market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6% through 2030, driven by consumer demand for healthier, customizable, and quick options. The U.S. market remains its core geography, but international expansion in Canada, Europe, and the Middle East is underway.
Secular Tailwinds Through 2030
Key drivers include digital transformation (mobile ordering, delivery, loyalty), menu innovation, and urban + suburban expansion. The company has guided toward 7,000+ total restaurants in North America, more than double its current footprint, and is targeting restaurant-level margins above 26%. Increasing consumer focus on sustainability, ingredient transparency, and value-for-money dining also favor Chipotle’s positioning.
Competitive Positioning
Qdoba and Taco Bell offer similar menu formats, but Chipotle’s ingredient sourcing and limited-time offers (e.g., brisket, barbacoa) create differentiation. Unlike most peers, Chipotle owns and operates nearly all its stores, allowing tighter operational control and consistency. Sweetgreen competes more on salads and health, while Shake Shack and Panera focus on different cuisines and mealtime occasions. Few brands match Chipotle’s digital scale and throughput efficiency.
Differentiation and Moat
Chipotle’s core differentiators include its vertically integrated supply chain for ethically sourced ingredients, tech-enabled operations (e.g., kitchen automation trials), and a highly profitable Chipotlane model. It also has one of the most loyal customer bases in foodservice, with over 40 million members in its loyalty program. Its commitment to operational simplicity and real food is a long-standing moat in an industry that struggles with labor, consistency, and quality.
Leadership and Management
Brian Niccol has served as CEO since 2018, previously leading Taco Bell. Under his leadership, Chipotle has embraced a tech-forward, margin-optimized playbook that revitalized growth. Jack Hartung, CFO since 2002, has been instrumental in maintaining strong unit economics and cash flow discipline. Curt Garner, Chief Customer & Technology Officer, leads digital, mobile, and loyalty initiatives that have driven Chipotle’s transformation into a digital powerhouse.
Financial Performance (Past 5 Years)
Chipotle has shown consistent top-line and bottom-line growth over the past five years. Revenue grew from $5.6 billion in FY2019 to an estimated $11.2 billion in FY2025, reflecting a CAGR of approximately 12%. Net income grew from $350 million in 2019 to over $1.4 billion in FY2024, delivering an earnings CAGR above 30%. Gross margins have expanded with price increases, improved throughput, and the scaling of Chipotlanes.
Strong Balance Sheet and Free Cash Flow
The company has no long-term debt and over $1.7 billion in cash and equivalents. It generates free cash flow well over $1 billion annually, fueling share buybacks and expansion without external financing. Its asset-light model (owning fewer real estate assets) also enhances return on invested capital (ROIC), which exceeds 30%.
Margin Leadership and Store-Level Economics
Chipotle boasts some of the best restaurant-level margins in the industry, with average unit volumes (AUVs) exceeding $3 million per location and restaurant-level margins north of 25%. This operational efficiency has allowed Chipotle to thrive even during periods of inflationary input costs and labor pressures.
Bull Case for CMG Stock
- Expansion runway with goal to grow to 7,000+ stores in North America
- Digital and Chipotlane growth driving higher AUVs and margins
- Strong free cash flow, no debt, and best-in-class ROIC
Bear Case for CMG Stock
- High valuation leaves little room for error on same-store sales growth
- Food inflation and wage pressures could erode margins
- International expansion risk and reliance on North American growth
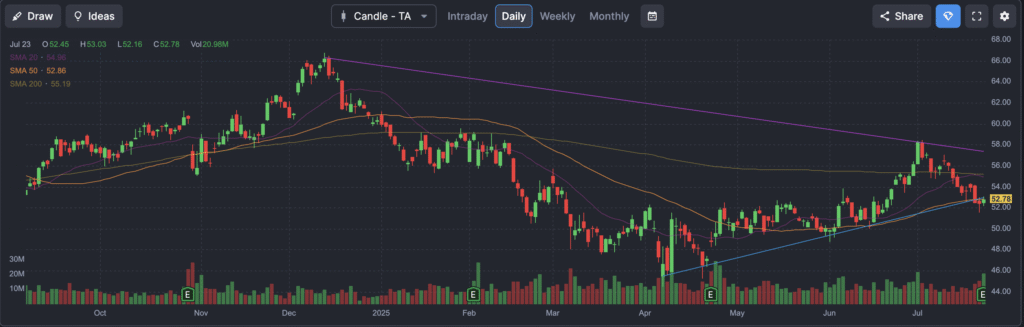
The stock is in a stage 4 bearish markdown on the monthly and weekly charts with support at the $43 range. The daily chart is negative as well. The valuation gives us pause to even wait for a reversal, so this might be a good stock to wait on to get to $40 – $43 for a long term entry.